Figure 3.
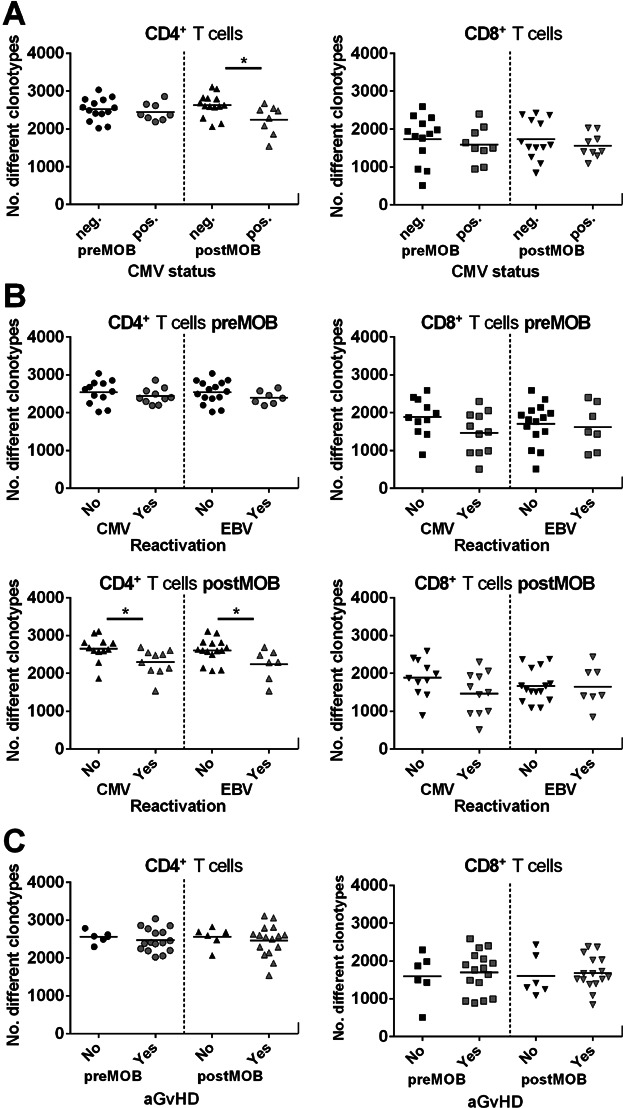
Donor TCRβ diversity and clinical correlation. (A) Diversity dot plots of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells of cytomegalovirus (CMV)-seropositive or -seronegative donors before (pre) and after (post) G-CSF mobilization. Only for the CD4+ T cell compartment postmobilization a significant difference could be displayed between CMV-seropositive and -seronegative donors (*p < 0.05; neg. n = 14; pos. n = 8). (B) Diversity dot plots of CD4+ and CD8+ TCRβ rearrangements of G-CSF–mobilized donors premobilization and postmobilization according to patients either reactivated (“Yes”) or not (“No”) with CMV (“Yes”: CD4+ n = 10; CD8+ n = 11) or Epstein–Barr virus (EBV; “Yes”: CD4+ n = 7; CD8+ n = 7). Cases with CMV and/or EBV reactivation presented significantly lower numbers of unique clonotypes in CD4+ T cells post–G-CSF mobilization (*p < 0.05). In CD8+ T cells, no significant difference could be detected for virus reactivation. (C) Diversity dot plots of CD4+ and CD8+ T cells of donor T cells premobilization and postmobilization according to patients who either exhibited acute graft-versus-host disease (aGvHD; “Yes”) or not (“No”). No significant correlation could be detected between donor T cell diversity and aGvHD appearance in patients.  CD4+ T cells preMOB;
CD4+ T cells preMOB;  CD4+ T cells postMOB;
CD4+ T cells postMOB;  CD8+ T cells preMOB;
CD8+ T cells preMOB;  CD8+ T cells postMOB.
CD8+ T cells postMOB.
