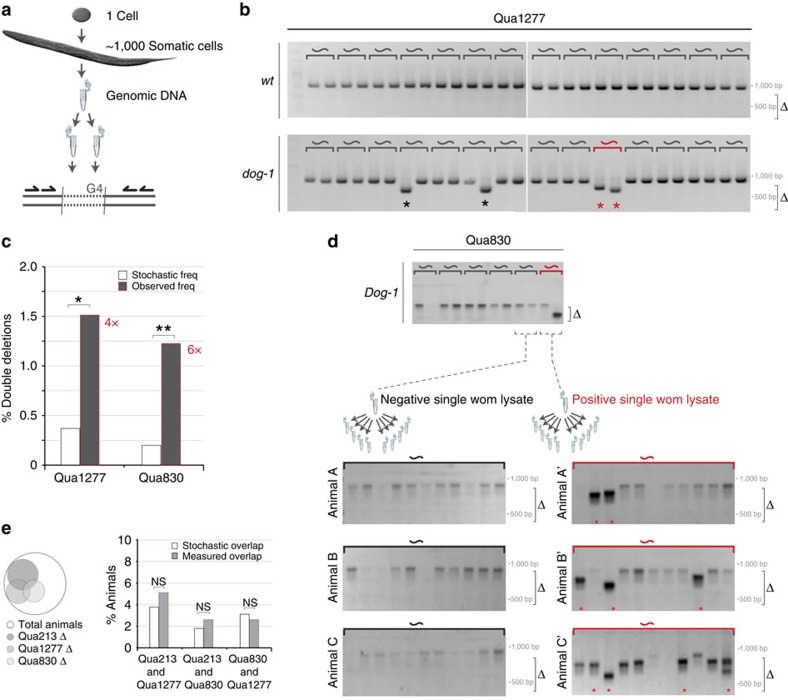
Figure 2. Overrepresentation of co-occurring G4 deletions in single animals.
(a) Schematic representation of PCR-based experimental setup to identify G-quadruplex-induced deletions in single animals. (b) PCR analysis of G-quadruplex-induced instability at endogenous G4 site Qua1277 in dog-1-proficient (upper panel) and -deficient animals (lower panel). Representative gel images display the result of single animals (∼) assayed twice independently. See Supplementary Fig. 7a for additional gel images. The size range of PCR-amplified deletion products is indicated by Δ; two reference size markers (500 and 1,000 bp) are indicated; asterisks mark positive reactions/unique deletion products. (c) Quantification of the number of single animals that had two differently sized deletion (observed freq.), which was compared with the expected random double deletion frequency (white bars) based on frequency of deletions determined within the tested animal population (see Methods section for details). Asterisks indicate highly significant overrepresentation of the observed double deletion events within the tested population (*n=352 and **n=576) as determined by hypergeometric testing (*P<0.003 and **P<0.001). (d) PCR analysis of G-quadruplex-induced instability at endogenous G4 site Qua830 in dog-1 animals, upper panel as in b. Single worm lysates were first categorized based on the presence or absence of a G4 deletion. Subsequently, the samples were assayed 11 times, to probe for the presence of additional G4 deletions. Three gel images representative for each category are depicted. Uncropped gel images are provided in Supplementary Fig. 7b. The size range of PCR-amplified deletion products is indicated by Δ; two reference size markers (500 and 1,000 bp) are indicated; asterisks mark uniquely sized deletion products (e) Venn diagram showing the distribution of G4 deletion events in 156 animals tested for all three loci. Histogram depicting the expected (white bars) and observed (black bars) frequency of animals showing a G4 deletion at both indicated G4 loci. NS indicates that the observed overlap does not statistically deviate from a random distribution, as determined by hypergeometric testing (P>0.20), which indicates that deletion events at different G4 loci are not interdependent.