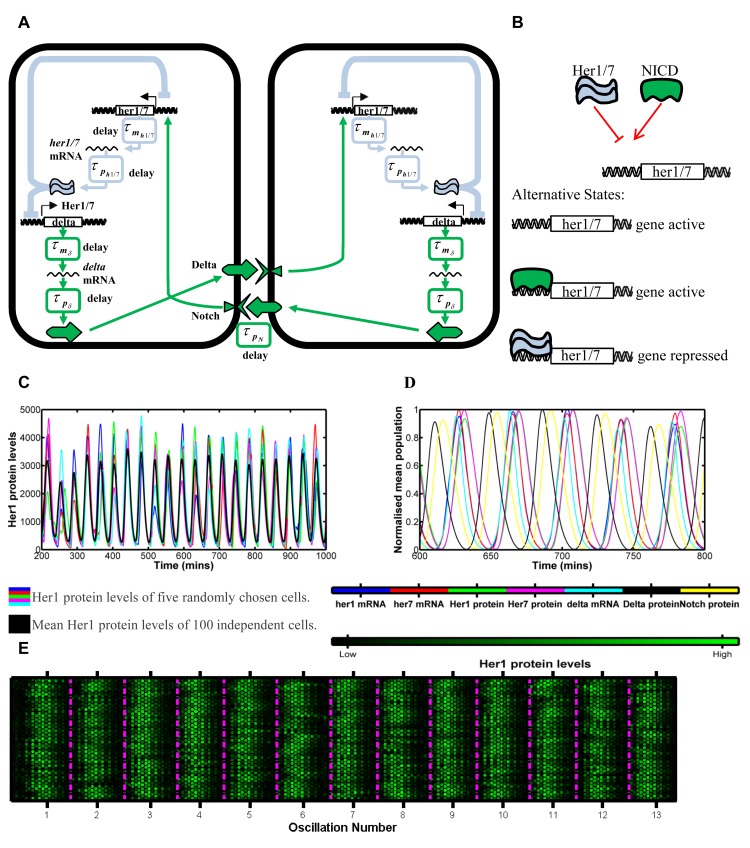
Fig 5. Modelling the effects of Notch signalling on the synchrony of neighbouring cell oscillations.
5A: Notch signalling network between neighbouring cells. The light blue section corresponds to the intra-cellular her1/7 feedback loop of Fig 1A. The green section corresponds to Notch inter-cellular signalling. Her1/7 protein inhibits expression of delta in addition to her1/7. Transcription and translation of delta occurs with respective delays and Delta activates Notch in the neighbouring cell and NICD is produced with delay, When Notch binds to the her1/7 genes this leaves them in an active state, influencing the her1/7 intra-cellular feedback loop. 5B: Competitive binding reaction kinetics of Her1/7 and Notch proteins to the sites on her1/7 DNA. When the her1/7 gene is free or bound to NICD then the gene is active. When Her1/7 binds to the her1/7 gene then expression of the gene is inhibited. It is these reaction kinetics that we model with a modified Gillespie Algorithm. 5C: Plot of oscillating Her1 levels versus time when Notch signalling has been incorporated into the model. The coloured lines correspond to five randomly selected individual cells; the black line corresponds to the mean of all 64 cells. The cells oscillate in synchrony. 5D: The normalised mean population levels of her1 mRNA, her7 mRNA, Her1 protein, Her7 protein, delta mRNA, Delta protein and Notch protein demonstrating the phase of each population. Notch is almost totally out of phase with Her1/7 so will be high when Her1/7 is low and vice versa. 5E:Plots of multiple cells oscillatory clocks versus time (compare to Fig 3). Each lattice is a single cell. Each five minute interval is marked by two columns of 32 cells. The mean phases of oscillation over all cells are marked by the magenta lines. The cells remain in synchrony throughout and generate well defined somites. The modelling demonstrates that Notch signalling is able to override the effects of stochastic gene regulation and keep neighbouring cell clocks oscillating in synchrony.