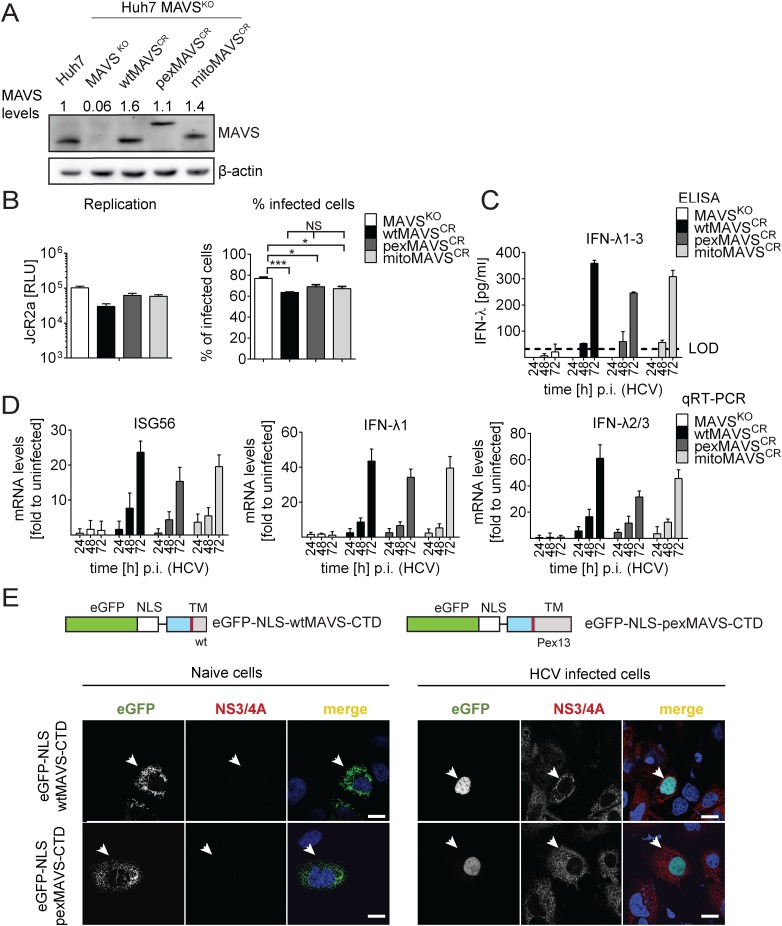
Fig 6. HCV activates type III IFN response via peroxisomal and mitochondrial MAVS to a comparable extent.
(A) Huh7 MAVSKO cell lines were generated using the CRISPR/Cas system. Cleavage resistant wt-, pex- and mitoMAVS were expressed in these cells by lentiviral transduction. Expression levels of the proteins were quantified by Western blot. Numbers above each lane refer to abundance of a given MAVS variant, normalized to β-actin and endogenous MAVS that was set to one. (B) Cell lines were infected with either the HCV reporter virus JcR2a (MOI = 1) or Jc1 (MOI = 1). Seventy two hours later HCV replication in JcR2a-infected cells was determined by luciferase assay whereas Jc1-infected cells were analyzed by NS5A-specific immunofluorescence. The percentage of infected cells was determined by counting at least 500 cells for each condition. (C) Cells were infected with the HCV isolate Jc1 (MOI = 5) and amounts of IFN-λ1–3 released into cell culture supernatants were determined by ELISA. The dashed line represents the limit of detection limit (LOD). N.d., not detectable. (D) Total RNA of infected cells was extracted and mRNA amounts of ISG56 and type III IFNs were determined by qRT-PCR. All data were normalized to GAPDH using the ΔΔct method and are expressed relative to uninfected control cells (set to 1). A representative experiment performed with technical triplicates is shown. Bars indicate the standard error. All experiments were conducted three times and with two additional Huh7 knockout cell clones. (E) Huh7 cells were infected with Jc1 (MOI = 5) and transfected 40 hours later with expression constructs encoding GFP-tagged CTD of wt- or pexMAVS (for construct design see Fig 2A). Note that HCV-mediated cleavage of the reporter results in nuclear accumulation of the eGFP signal. White arrow indicates an HCV infected cell. Scale bar, 20 μm.