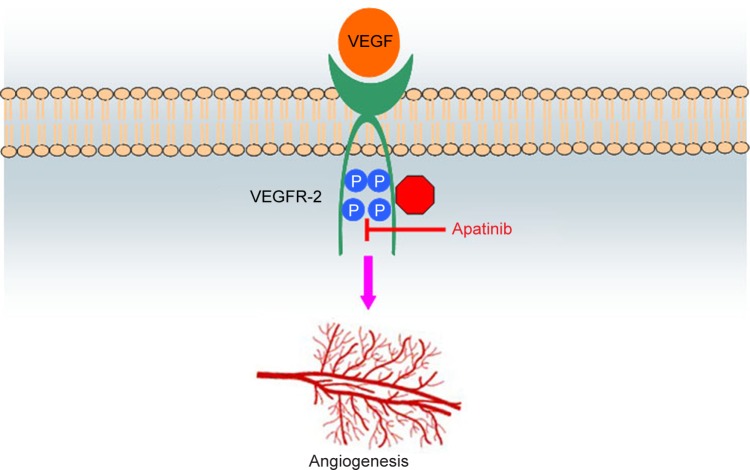
Figure 2.
Schematic illustration of the possible mechanism of apatinib as the inhibitor of VEGFR-2.
Notes: By specifically binding to the phosphorylation sites of VEGFR-2, apatinib inhibits the subsequent effects on the vascular endothelium, including cell proliferation, migration, permeability, and survival. Through this inhibition, apatinib plays an antiangiogenic role.
Abbreviations: VEGFR-2, vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2; VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor.