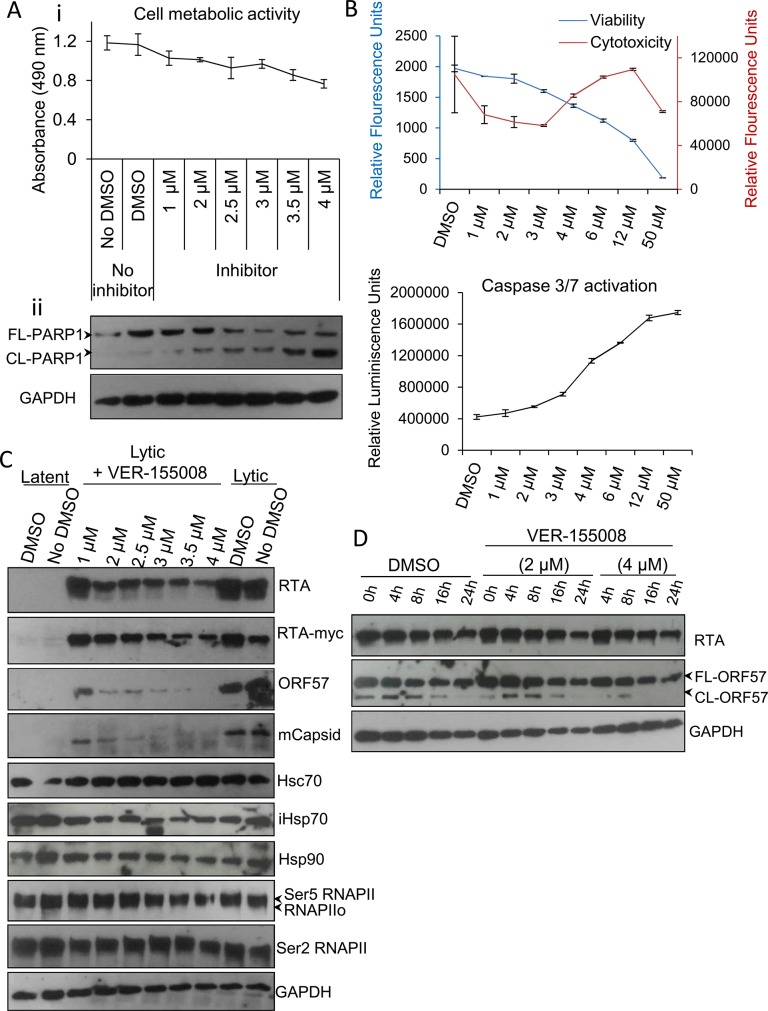
Fig 3. VER-155008 abrogated viral protein synthesis pre-translationally in TREx BCBL1-RTA cells.
(A) Cytotoxicity of VER-155008 was assessed in unreactivated cells exposed to increasing inhibitor concentrations for 24 h. (i) Cell metabolic activity was reduced in a dose-dependent manner as quantified using an MTS assay. (ii) A dose-dependent cleavage of full length (FL) PARP1 protein into cleaved (CL) PARP1 was observed in the presence of VER-155008. (B) Unreactivated cells were exposed for 24 h to increasing inhibitor concentrations. Concentrations higher than 3 μM resulted in increased cytotoxicity and activation of effector caspases-3/7 as demonstrated by quantification with ApoTox-Glo Triplex Assay. (C) Immunoblot analysis showing that reactivated cells treated with non-cytotoxic inhibitor concentrations (1 to 2.5 μM) for 24 h revealed a decrease in viral proteins compared with DMSO-treated samples while cellular proteins remained unaffected. RNAPIIo denotes hypophosphorylated RNAPII. Ser5 and Ser2 RNAPII denote serine 5- and serine 2- hyperphosphorylated RNAPII forms respectively. (D) Cells were reactivated for 24 h to allow robust viral protein production. Then, DMSO control (0.1%) or VER-155008 was added in conjunction with cycloheximide (CHX) at 50 μg/ml to block de novo protein synthesis. Protein lysates were collected at several times post-CHX addition (0, 4, 8, 16 and 24 h) and analysed by Western blotting. VER-155008 did not alter the half-life of RTA or ORF57 protein, thus these proteins were not clients of Hsp70 isoforms.