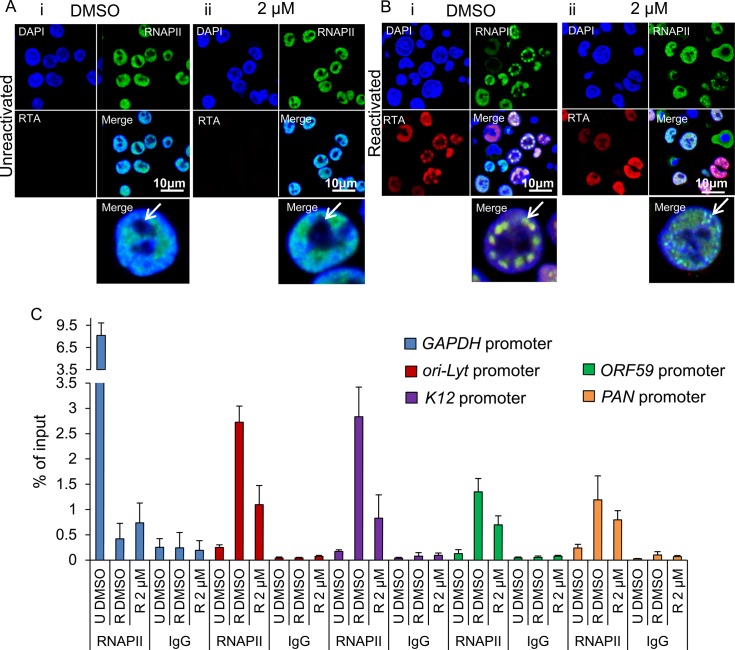
Fig 9. Inhibition of Hsp70 isoforms curtailed RNAPII relocation to KSHV RTCs.
(A) TREx BCBL1-RTA cells remained unreactivated and treated with control DMSO (0.1%) (i) or 2 μM VER-155008 (ii). A polyclonal antibody against RTA and a monoclonal antibody (CTD4H8) against RNAPII were used for immunoflourescence analysis. RNAPII protein was nuclear excluding the nucleoli (arrows) regardless of inhibitor treatment. (B) TREx BCBL1-RTA cells were reactivated and treated with either control DMSO (0.1%) or 2 μM VER-155008 for 24 h. In DMSO-treated cells RNAPII and RTA were recruited to viral RTCs (i arrow) while in inhibitor-treated cells RTA was diffuse in the nucleus and RNAPII formed numerous small foci that excluded the nucleoli and resembled pre-replicative sites (ii arrow). (C) TREx BCBL1-RTA cells were either reactivated (R) in the presence of DMSO (0.1%) or 2 μM VER-155008 for 24 h. Unreactivated (U) cells treated with DMSO (0.1%) were used to assess levels of lytic reactivation. ChIP assays were carried out with either monoclonal CTD4H8 RNAPII antibody or mouse control antibody (IgG). In the presence of VER-155008, significantly reduced amounts of RNAPII bound to viral promoters were detected. The average of three independent experiments is shown with error bars as standard deviation.