Figure 4. Synaptic connections of bipolar tail neurons.
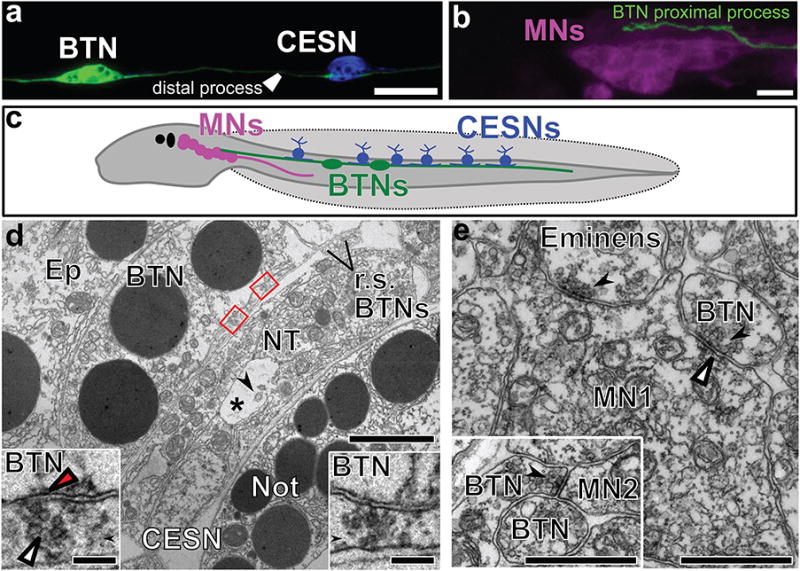
a, Bipolar tail neuron (BTN) labeled by Glutamate decarboxylase>unc-76∷eGFP (green) contacting a caudal epidermal sensory neuron (CESN) labeled by Slc17a6/7/8(Vglut)>unc-76∷mCherry (blue). b, Proximal process of BTN labelled by Islet BTN>unc-76∷mCherry (green) contacting motor ganglion neurons (MNs) labelled by Fgf8/17/18>unc-76∷eGFP (magenta). c, Diagram of Ciona larva showing synaptic connections between CESNs in tail epidermis, BTNs, and MNs. d, Two synaptic inputs (red boxes, insets) from the sheet-like profile of a CESN to a left-side BTN; Transmission electron micrograph from wide-area montage. The profile of a second BTN axon lies out of view. Axon profiles from two right-side BTN axons (r.s. BTNs) are visible. BTNs overlie the neural tube (NT) with neural canal (*) and cross-sectioned cilia (arrow). An epidermal cell (Ep) overlies the BTN. Each synapse enlarged in inset has ∼52 nm diameter presynaptic vesicles (white arrowhead), and the left synapse has a postsynaptic density (red arrowhead). Scale bars 1μm and (insets) 0.5 μm. Not, notochord. e, Synaptic input (arrow) from a BTN to the axon of a member of the most anterior pair (A11.118) of motor neurons (MN1), identified by a cumulus of ∼60-nm presynaptic vesicles and a shallow postsynaptic density (arrowhead). A second input nearby originates from the axon of an Eminens neuron12 (arrow). Inset: Synaptic input from BTN to the axon of a second pair of motor neurons (MN2). Scale bars, 1μm.
