Extended Data Figure 4. Spatiotemporal restriction of Neurogenin expression.
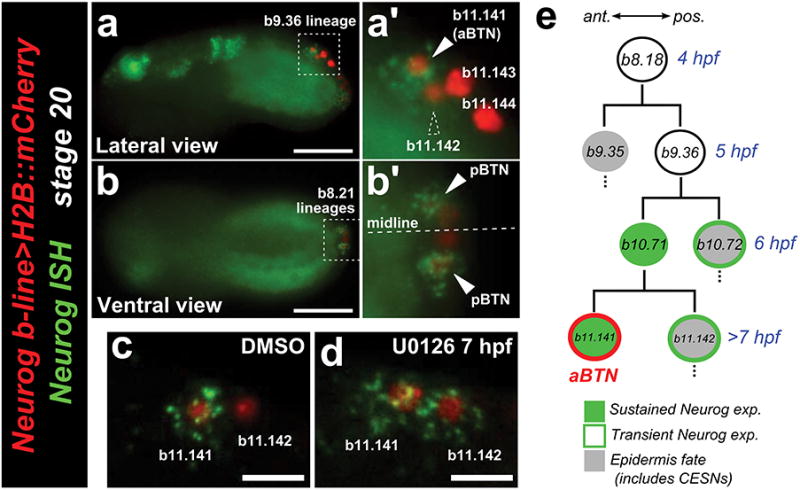
a, Lateral view of in situ hybridization (ISH) for Neurogenin (Neurog, green) in embryo electroporated with Neurog b-line>H2B∷mCherry (red) shows that Neurog expression is selectively maintained in only a subset of initially Neurog-expressing neural plate border cells. a′, In the b9.36 lineage, the anterior-most cell (b11.141, solid arrowhead) is always the sole one to express Neurog at this stage, and will go on to become the anterior bipolar tail neuron (aBTN). Dashed arrowhead indicates b11.142, the sister cell of b11.141, which has downregulated Neurog relative to its sibling. b, b′, The identities of the cells in the tail tip (presumed b8.21-derived) lineages are unclear, but Neurog is similarly restricted (arrowheads) to a single cell on either side of the midline, which we interpret as the definitive posterior BTNs (pBTNs). c, Control embryo treated with DMSO vehicle, showing wild-type pattern of Neurog expression only in b11.141. d, Neurog is expanded to b11.142 upon treatment with the MEK inhibitor U0126 at 7 hpf. This condition also results in specification of supernumerary BTNs, presumably due to expanded Neurog expression (see text for details). Thus, downregulation of Neurog in b11.142 also requires MEK/ERK signaling. e, Diagram of the aBTN lineage, descended from the b8.18 blastomere. Scale bars in a,b 25 μm. Scale bars in c,d 10 μm.
