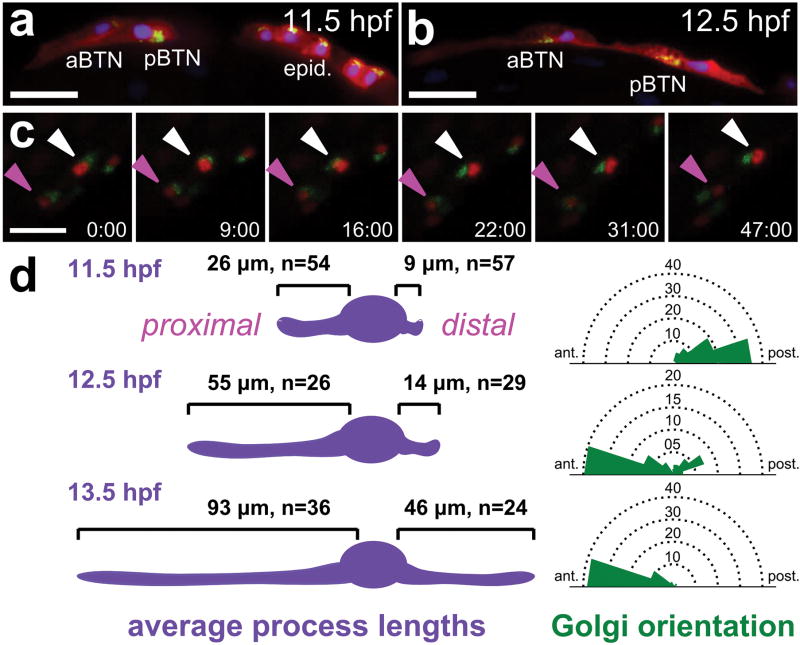
Extended Data Figure 6. Cell polarity and morphogenesis of bipolar tail neurons.
a, Embryo at 11.5 hpf (18°C) with bipolar tail neurons (BTNs) displaced from clonally related epidermal cells (“epid.”) labeled by UNC-76∷VenusYFP (red), Galnt7ΔC∷CFP (green), and H2B∷mCherry (blue) driven by Neurogenin b-line cis-regulatory module. Targeted localization of CFP by the Galnt7 N-terminal signal sequence reveals polarized subcellular distribution of Golgi apparatus on posterior side of BTN nuclei as migration and proximal process extend in an anterior direction. This is distinct from the apical (dorsal) location of the Golgi apparatus in epidermal cells. b, Embryo at 12.5 hpf (18°C) showing 180° inversion of Golgi apparatus localization to the anterior side of the nucleus, immediately preceding distal process extension. Scale bars in a,b 50 μm. c, Still frames from a confocal image stack time lapse movie (Supplementary Video 4) showing inversion of Golgi complex (Galnt7ΔC∷VenusYFP, green) relative to nuclei (H2B∷mCherry, red) in migrating BTNs. Time lapse imaging initiated at 11.5 hpf (18°C). Time in minutes elapsed from start shown at bottom right of each panel. Anterior BTN (aBTN) indicated by magenta arrowhead, posterior BTN (pBTN) indicated by white arrowhead. Scale bar, 25 μm. d, Diagram showing correlation of average length of proximal (left) and distal (right) processes and angle of Golgi apparatus location relative to cell nucleus along the anterior-posterior axis in BTNs at different time points. Locations of Golgi apparatus represented by rose plots of bins of 20° spanning anterior (0°) and posterior (180°) endpoints around dorsal edge of BTN nucleus. Bin diameters indicate number of cells. Embryos analyzed belong to the same pool as embryos in a,b. See Supplementary Table 1 for source data.