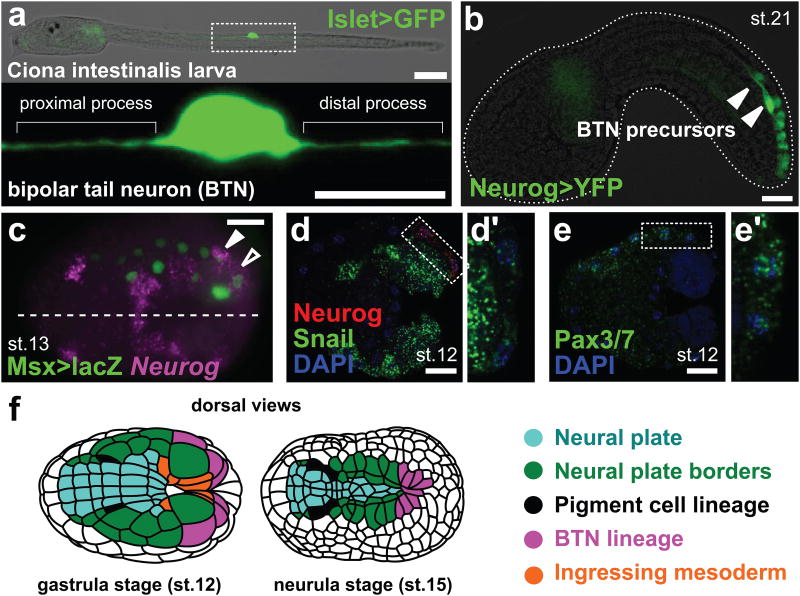
Figure 1. Bipolar tail neurons come from the borders of the neural plate.
a, Larva with a bipolar tail neuron (BTN) labeled by Islet BTN>unc-76∷eGFP (green). Lower panel: enlarged view of BTN above. Scale bars 75 μm (upper), 25 μm (lower). b, Migrating BTN precursors (arrowheads) labeled by Neurog b-line>unc-76∷Venus (green). Scale bar, 25 μm. c, In situ hybridization (ISH) for Neurog (magenta) in embryo electroporated with Msx>nls∷lacZ plasmid (immunolabeling of β-galactosidase in green). White arrowhead: Msx+/Neurog+ BTN progenitor. Black arrowhead: transient Neurog expression in BTN progenitor's sister cell (epidermal progenitor). Dashed line: midline. Scale bar, 25 μm. d, ISH for Neurog (red) and Snail (green). Scale bar, 25 μm. Box enlarged in d′ showing low levels of Snail expression in BTN progenitor. e, Pax3/7 ISH (green). Scale bar, 25 μm. Box enlarged in e′ showing Pax3/7 expression in BTN progenitor. f, Adapted illustration17 of embryos showing position of pigment cell and BTN progenitors (and their descendants) in the neural plate borders. Lateral views in a,b, dorsal views in c-f. Anterior to the left throughout. st. = stage.