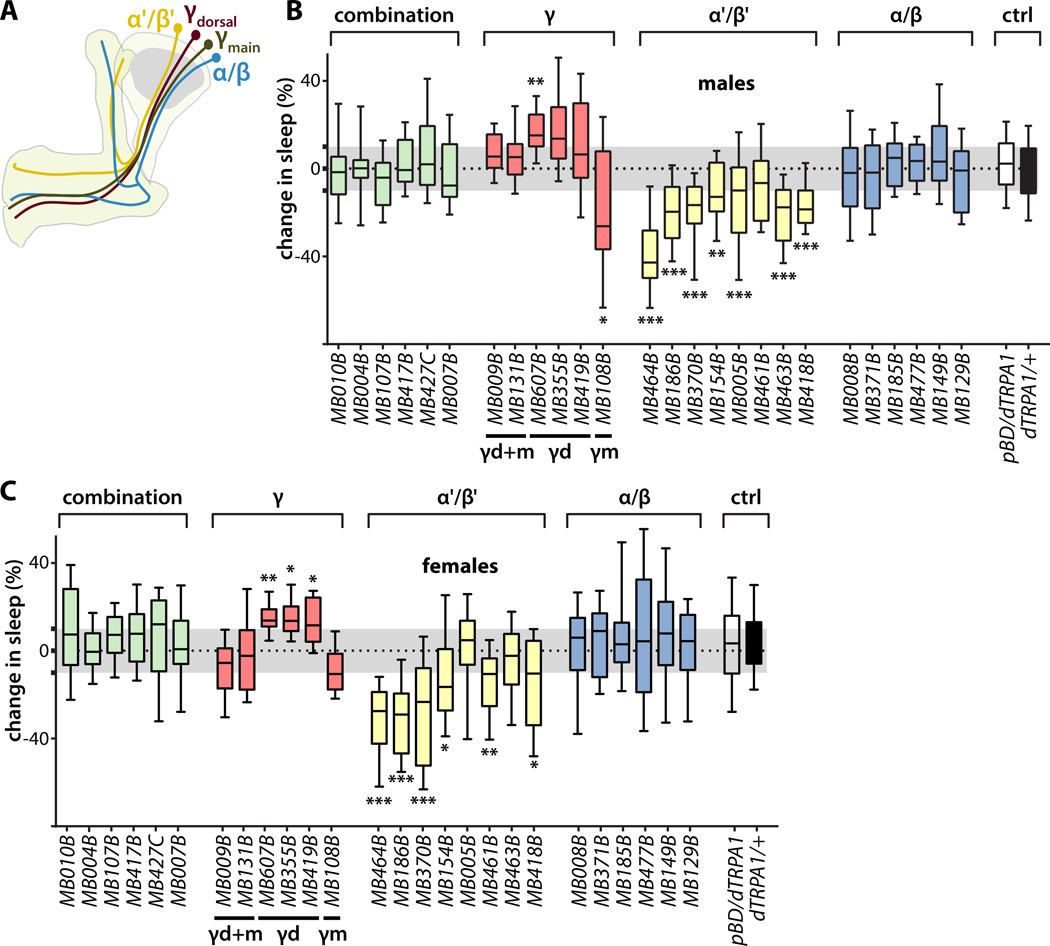
Figure 1. Identification of sleep-promoting and wake-promoting KCs.
(A) Schematic representation of the MB showing the lobe-specific axon projections of the indicated classes of KCs. Axons of α'/β' and α/β KCs bifurcate to innervate the vertical α' and α lobes and horizontal β' and β lobes, while the axons of γ KCs do not bifurcate and innervate only the horizontal γ lobe.
(B) Change in sleep of male flies induced by activation of KC subsets targeted by the indicated split-GAL4 driver lines to express the dTRPA1 temperature-gated depolarizing cation channel. Percent change in sleep is defined as (sleep on day 1 – sleep on day 2) / sleep on day 1, where the ambient temperature is increased on day 2 from 21.5 °C to 28.5 °C to activate the neurons expressing dTRPA1. Activation of either α'/β' or γmain (γm) KCs promoted wake, while activation of γdorsal (γd) KCs promoted sleep. Midline, box boundaries, and whiskers represent median, quartiles, and 10th and 90th percentiles, respectively. Split-GAL4 lines are grouped by the indicated lobe-specific projections of their targeted KC subsets. Each split-GAL4 line was compared to an enhancerless GAL4 (pBDPGAL4U, indicated in the figures as pBDG4U or pBD) by Kruskal-Wallis non-parametric one-way ANOVA and Dunn's post-hoc correction for multiple comparisons (*, p<0.05; **, p<0.01; ***p<0.001; n=24–46 flies per genotype).
(C) Change in sleep of female flies, as in (B).