Fig. 7.
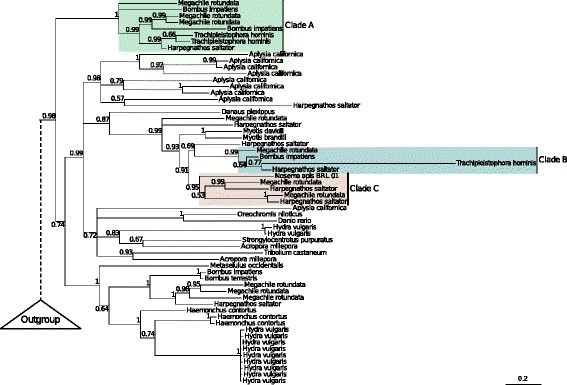
Phylogenetic analysis of PiggyBac transposons suggests a natural insect host for T. hominis. A Bayesian phylogeny of T. hominis PiggyBac transposases inferred under the C20 model [117] in PhyloBayes [118]. Support values are Bayesian posterior probabilities, and branch lengths are proportional to the expected number of substitutions per site. The tree topology supports two recent, independent transfers of PiggyBac elements from hymenopteran insects into T. hominis. In both cases, the ant Harpegnathos saltator is recovered as the closest relative of the T. hominis sequence, although with variable posterior support. We also identify a transfer from insects into the microsporidian Nosema apis, a honeybee parasite. Clade A – An insect clade including two T. hominis PiggyBac elements, as identified in [10]. Clade B – A distinct clade of insect elements, including the newly discovered T. hominis PiggyBac element. Clade C – Clade including Nosema apis and insect PiggyBac elements
