Figure 2. Rapid stereociliary fascin 2b exchange transpires without a phosphointermediate.
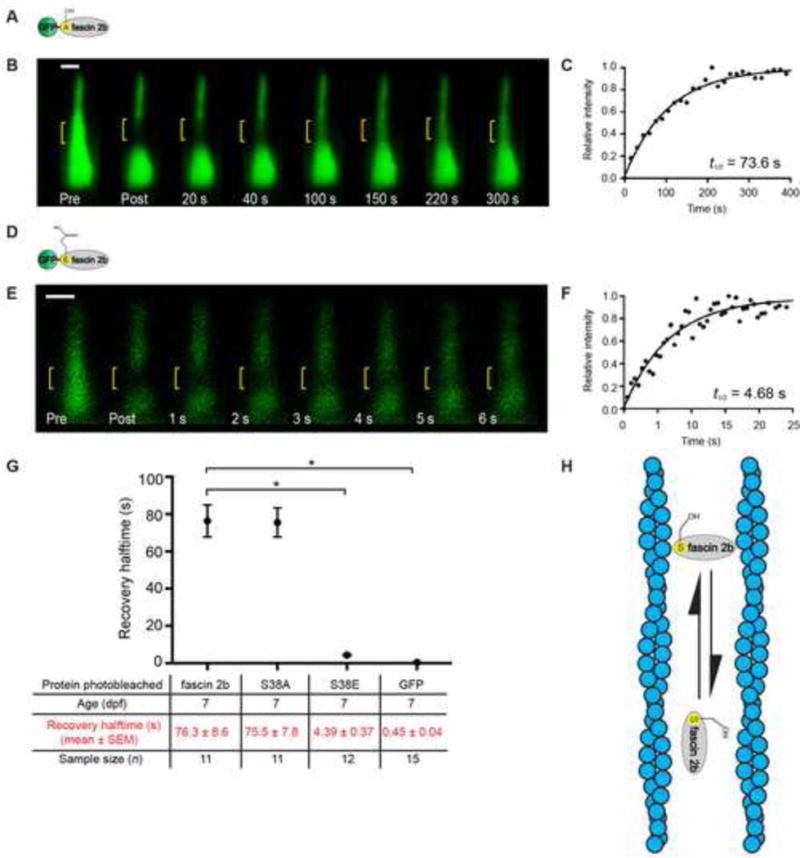
(A) Phosphomutant GFP-S38A fascin 2b schematic. (B) Qualitative FRAP series of a hair bundle containing GFP-S38A fascin 2b before (Pre) and after photobleaching (yellow bracket). (C) Recovery plot from a hair bundle containing GFP-S38A fascin 2b from a quantitative FRAP series in Figure S1F, t1/2 = 73.6 s. (D) Phosphomimetic GFP-S38E fascin 2b schematic. (E) Bundle containing GFP-S38E fascin 2b before (Pre) and after photobleaching. (F) Recovery plot of E demonstrates exceedingly fast recovery, t1/2 = 4.68 s, of the phosphomimetic relative to wild-type fascin 2b. (G) Summary of recovery halftimes for GFP-fascin 2b, GFP-S38A fascin 2b (S38A), GFP-S38E fascin 2b (S38E), and GFP. Since GFP-S38A fascin 2b has a similar t1/2 value to GFP-fascin 2b, wild-type fascin 2b does not transition through a detectable phosphointermediate in stereocilia. *P< 0.0001 (Student’s t test) indicates statistically significant. Fish used were 7 dpf. Scale bars are 1 μm. (H) Model: The fascin 2b-F-actin binding cycle is independent of phosphorylation. In model, horizontally oriented fascin 2b protein indicates protein bound to F-actin. Vertically oriented fascin 2b protein is not bound to F-actin. Alternative model is shown in Figure S3B. See also Figure S3 and Tables S1 and S3.
