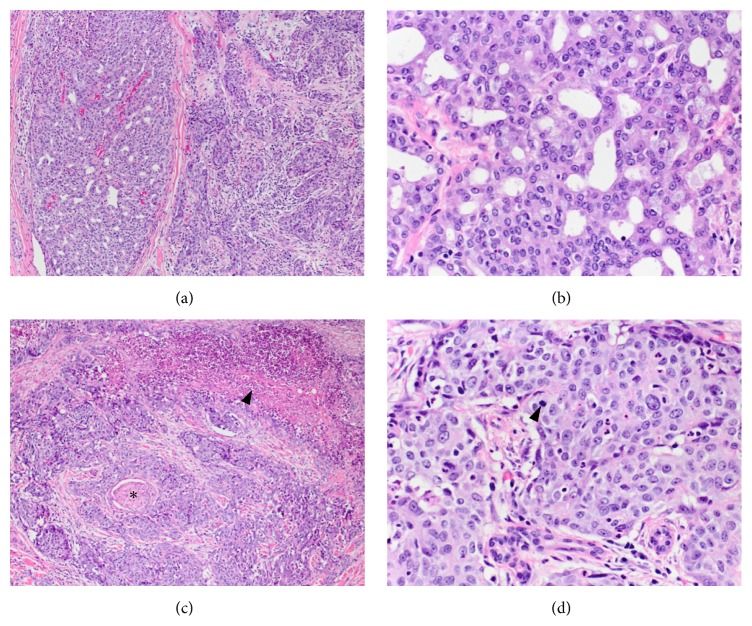
Figure 1.
Acinic cell carcinoma of the parotid gland. (a) The tumor exhibits two distinct areas on histologic examination. The two areas are juxtaposed to each other and there is no evidence of transition. On the left, the well-differentiated area shows glandular architecture and the area on the right side of the image shows an infiltrative growth pattern associated with prominent stromal response. H&E, 10x. (b) Higher magnification of the well-differentiated area demonstrates polygonal cells without significant cytologic atypia, variably basophilic granular cytoplasm, minimal pleomorphism, and inconspicuous mitotic activity. H&E, 40x. (c) Dedifferentiated regions of the tumor show focal necrosis (arrowhead) and multiple foci of perineural invasion (star) H&E, 10x. (d) Cytologically, the dedifferentiated areas display more pronounced pleomorphism and increased mitotic activity (arrowhead) H&E, 40x.