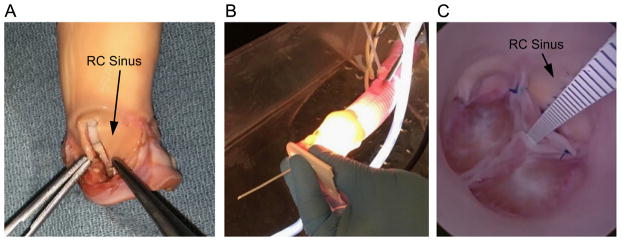
Fig. 4.
(A) Porcine model of congenital AR is created by resecting a 5 mm wide rectangular strip from the wall of the right coronary (RC) sinus, and approximating the cut edges with a running suture. The RC leaflet, which has been excised in the photo, is trimmed along its cut edge and reattached. (Note: aorta has been inverted to facilitate the procedure.) (B) The porcine aorta is attached to a Dacron tube through which the endoscope is inserted for visualizing the pressurized valve. (C) A plastic scale inserted through the closed valve is used to measure central coaptation height.