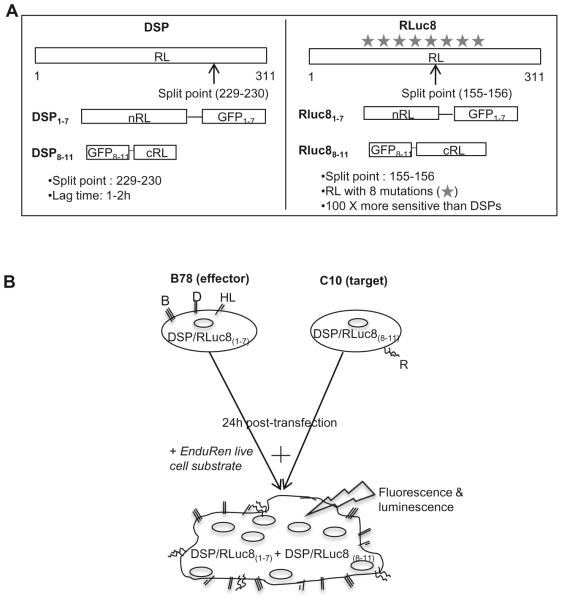
Figure 2. Schematic representation of the split luciferase assay and the constructs used.
(A). Constructs. Both renilla luciferase (RL) and green fluorescent protein (GFP) were split into inactive halves. The N-terminal region of RL was paired with the inactive N-terminal region of GFP. The second half of GFP was cloned to the C-terminal fragment of RL. Two generations of reporter genes were generated (DSP and RLuc8) that are different in the split point in RL and the presence of several mutations in RL ( ) that make luciferase brighter. The weak interaction of the RL halves is augmented by split-GFP and ensures a high efficiency in the recovery of RL activity. (B). Assay. In the HSV system, effector cells are transfected with gB, gD, gH, gL and the plasmid encoding one half of either the DSP or Rluc8 gene. Target cells, bearing receptor are transfected with the other half of the DSP or Rluc8 reporter genes. 24 hours post-transfection, EnduRen substrate is added and target and effector cells are mixed, so that upon fusion, the two inactive halves of DSP or Rluc8 can come together to produce fluorescence and luminescence.