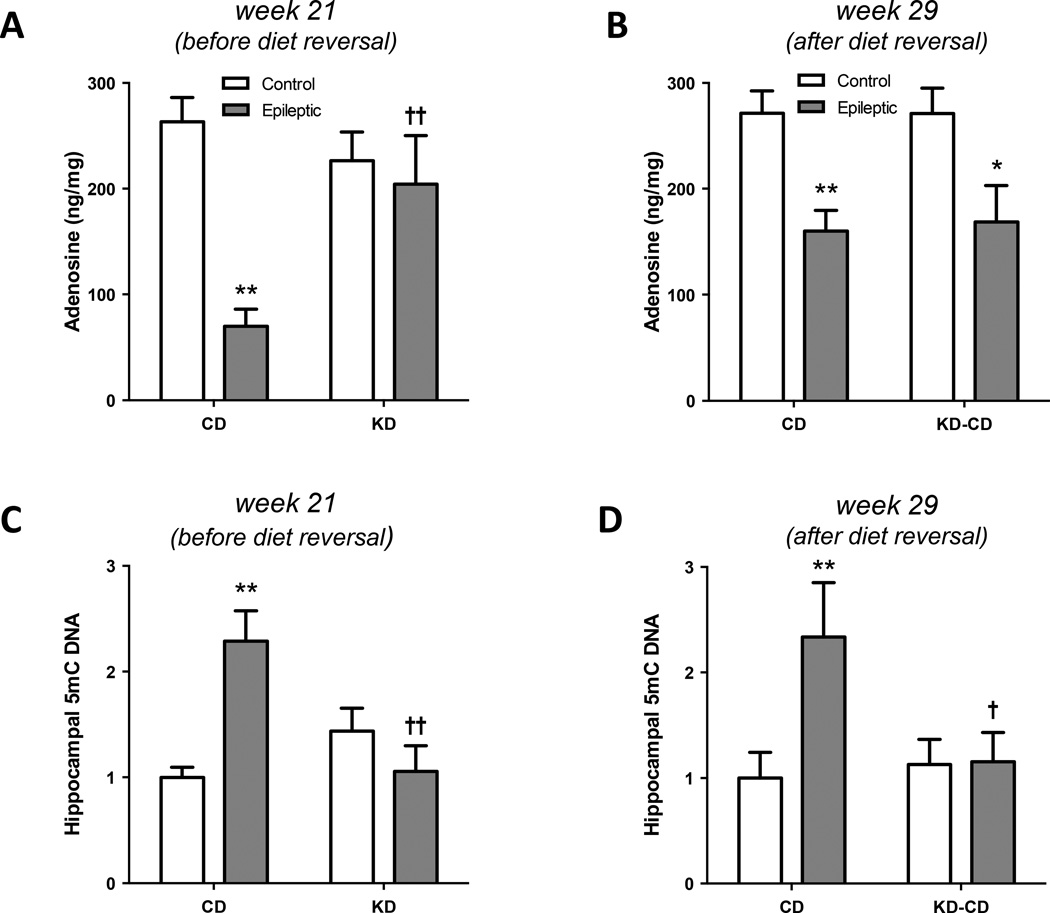
Figure 4. Hippocampal adenosine and 5-methylcytosine content.
(A) Hippocampal adenosine levels were measured from control or epileptic animals fed a CD or KD. Adenosine deficiencies in the epileptic CD-fed rats were reversed in the KD-fed rats (**P < 0.01 vs Control-CD, †† P < 0.01 vs Epileptic-CD). (B) Hippocampal adenosine levels from control or epileptic animals fed a CD or reversed to CD following KD treatment. (**P < 0.01, *P < 0.05 vs diet-matched Control). (C) Hippocampal 5-mC DNA from control or epileptic animals fed a CD or KD. DNA hypermethylation observed in the epileptic CD fed rats was reversed in the epileptic KD-fed rats (**P < 0.01 vs Control-CD, †† P < 0.01 vs Epileptic-CD). (D) Hippocampal 5-mC DNA from control or epileptic animals fed a CD or diet reversed following KD treatment (KD-CD). DNA 5-mC levels were maintained at control levels in the diet reversed (KD-CD) group (**P < 0.01 vs Control-CD, † P < 0.05 vs Epileptic-CD).