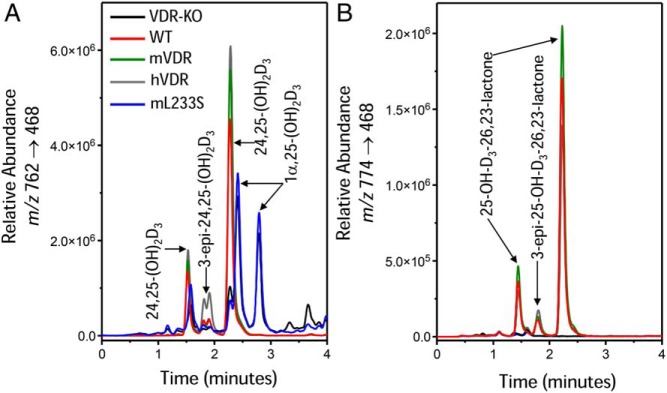
Figure 5.
LC-MS/MS-based vitamin D metabolic profiles of serum extracts of normal and VDR null mice on chow diet expressing either mVDR, hVDR, or the L233S-hVDR for their corresponding BAC transgenes mutant hVDRs. Vitamin D metabolites are extracted, derivatized with DMEQ-TAD, and then subjected to LC-MS/MS as described in Materials and Methods. Depicted are selected MRMs representing (A) the dihydroxyvitamin D3 daughter fragments at m/z 762→468 and (B) the 25-OH-D3-26,23-lactone daughter fragment at m/z 762→468. Note that each vitamin D metabolite generates 2 adduct peaks when derivatized with DMEQ-TAD; the peaks can be resolved on the LC column. Retention times of metabolites are provided in the text based upon authentic standards.