Figure 1.
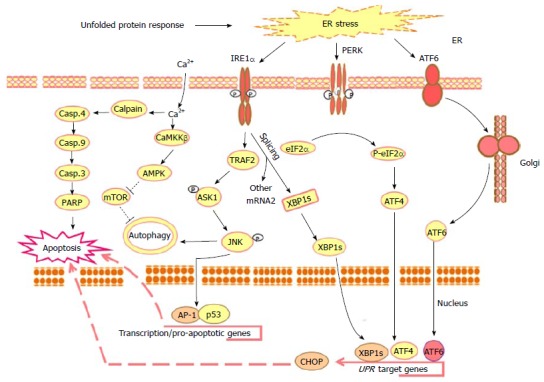
Outline of the main unfolded protein response-mediated mechanisms in response to the molecular action of anti-cancer agents. Upon the accumulation of misfolded proteins in the ER lumen, chaperones, the ER stress sensors PERK, IRE1α and ATF6 become active. The phosphorylation of PERK allows it to assemble in a homo-dimer to form an active form that, in turn, results in the phosphorylation of eukaryotic initiation factor2α (eIF2α) to initiate UPR downstream response leading to reduction of the protein overload to ER by the suppression of the translation and activation of ATF4 together with ER stress associated transcription factors such as, CHOP, PERK, IRE1 and ATF6. Activated PERK phosphorylates the translation initiation factor eIF2α to decrease the protein synthesis and enhance stress-inducible messages, such as ATF4. During ER stress the ATF6 traffics to the Golgi apparatus, where it is cleaved by S1P/S2P proteases. The cleavage of ATF6 from the Golgi membrane facilitates its localization to the nucleus, where it enhances the transcriptional up-regulation of UPR target genes leading to apoptosis. Whereas, activated IRE1α is implicated into several functions: One of these functions is essential to drive the splice mechanism of the XBP-1 mRNA to allow the translation of mature XBP-1 protein that, in turn, functions as a transcription factor to promote the transcription of UPR target genes such as CHOP leading to apoptosis; the other function of the activated IRE1α is to recruit TRAF2 that subsequently mediates the phosphorylation of ASK1 and the activation of its downstream JNK leading to the activation of the transcription factors AP-1 and p53 that are essential for the transcription of the pro-apoptotic genes and genes implicated in the processes of autophagsome formation and autophagy. UPR results also in intracellular calcium release leading to cell death via Calpain/Caspase-4, Caspase-9, caspase-3 and PARP axis or autophagy via CaMKKβ/AMPK axis leading to the inhibition of mTOR and subsequently autophagy. ER: Endoplasmic reticulum; PERK: Protein kinase RNA-like endoplasmic reticulum kinase; IRE1α: Inositol-requiring protein 1; ATF6: Activating transcription factor 6; UPR: Unfolded protein response; XBP-1: X-box binding protein 1; CHOP: CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein (C/EBP) homologous protein; TRAF2: TNF receptor-associated factor 2; ASK1: Apoptosis signal regulating kinase 1; JNK: C-jun-N-terminal kinase; PARP: Poly (ADP-ribose) polymerase; CaMKKβ: Calmodulin-dependent protein kinase kinase-β; AMPK: AMP-activated protein kinase; mTOR: Mammalian target of rapamycin.
