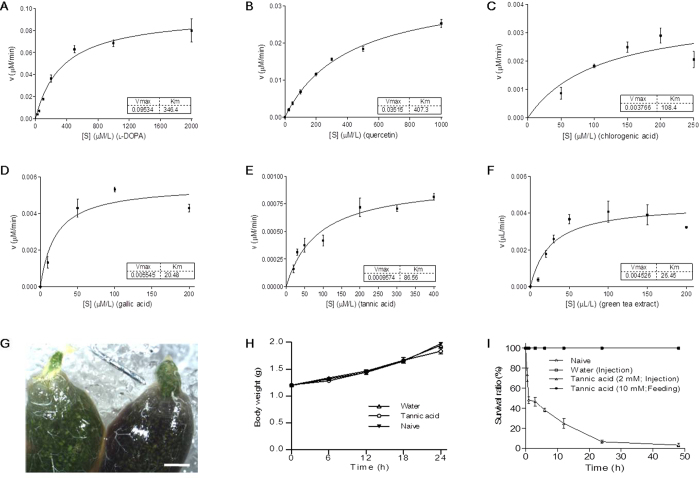
Figure 6. Plant phenolics are substrates for insect PPOs.
(A–F) Enzyme kinetics were measured using different phenolics as substrates. Each substrate at the indicated concentrations was mixed with ethanol-activated rPO1 (0.5 μg). Maximum absorbances were read at wavelengths specific to the products of each substrate (see Material and Methods for detail). The calculated Vmax and Km values are indicated in each figure. (G) Food in the foregut and fore-midgut did not become melanized unless the larvae were placed on ice for 2 h to stop gut motility. No melanization was observed in a freshly dissected gut (0 h). (H) Tannic acid was non-toxic following feeding to silkworm larvae. Larvae (IV-1) were fed mulberry leaves supplemented with 10 mM tannic acid or water (control) and weighed every 6 h. Each group consisted of 10 individuals. (I) Tannic acid (2 mM; 20 μl) or sterile water (20 μl) was injected into the hemocoel of silkworm larvae (IV-1), or larvae were fed mulberry leaves coated with 10 mM tannic acid, as described above. The survival ratios were calculated at the indicated times. Columns represent the means of three independent measurements ± S.E. Each group consisted of 10 (H) or 20 (I) individuals. Bar, 2.5 mm.