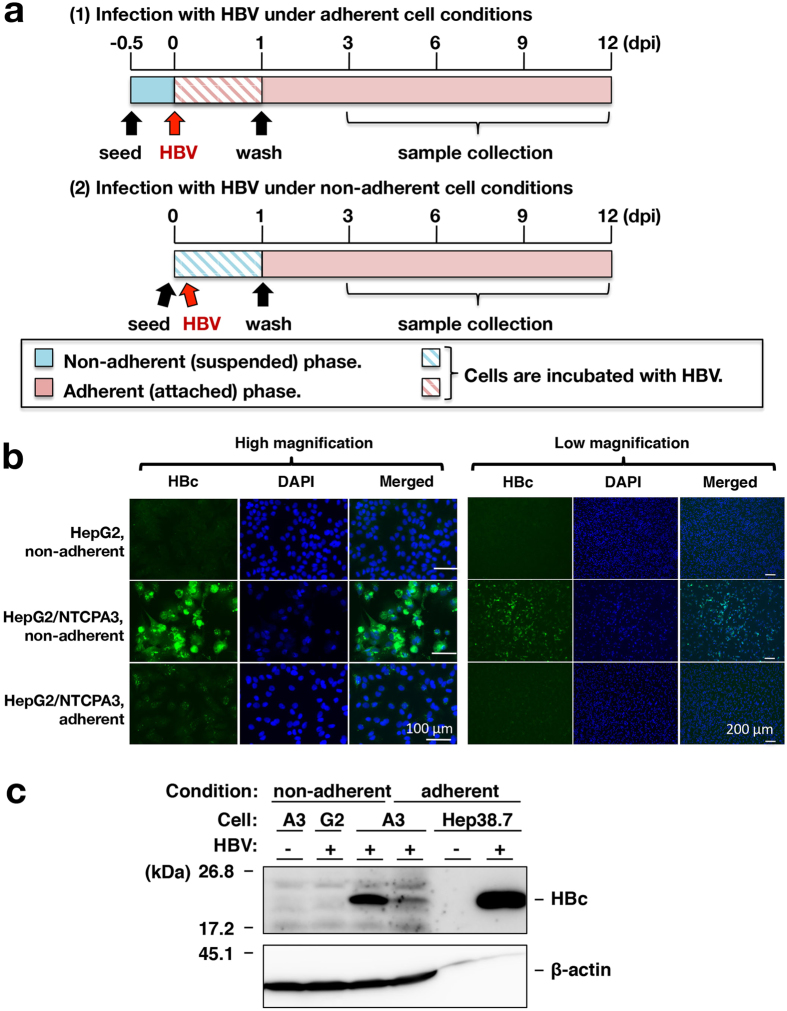
Figure 2. Enhancement of HBV infectivity by non-adherent cell conditions of infection.
(a) Procedures for HBV infection of adherent (top) and non-adherent cells (bottom) are schematized. Non-adherent (suspended cells; blue bar) or adherent cells (attached cells; red bar) were infected with HBV by the method described in Materials and Methods. (b) HepG2 or HepG2/NTCPA3 cells were infected with HBV at 1,000 GEq/cell in non-adherent or adherent phase. Infected cells were fixed at 12 dpi and then stained with an antibody to HBc, and counterstained with DAPI. These cells were observed under a fluorescence microscope. (c) Non-adherent HepG2 cells, non-adherent HepG2/NTCPA3 cells, or adherent HepG2/NTCPA3 cells were infected with HBV at 1,000 GEq/cell and harvested at 12 dpi. The lysates of these cells and mock-infected non-adherent HepG2/NTCPA3 cells were subjected to Western blotting using an antibody to HBc. The lysate of Hep38.7-Tet cells maintained with (HBV: −) or without tetracycline (HBV: +) was applied together as a negative or positive control of molecular size. G2; HepG2 cells, A3; HepG2/NTCPA3 cells. Original blots are presented in Supplementary Figure 1.