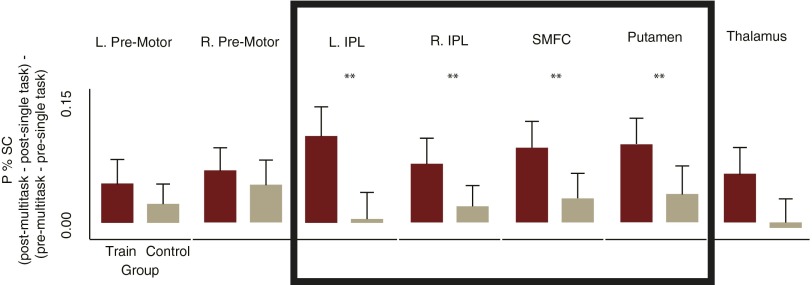
Fig. S4.
The FP-SC system. Of the seven brain regions that showed an influence of training [peak percentage signal change session × condition (mean single-task vs. multitask) interaction for the training group], only the regions within the boxed area [left and right inferior parietal lobules (L/R IPL), superior medial frontal cortex (SMFC); putamen] showed changes that were significantly larger for the training group (n = 50) relative to the control group (n = 50). Bar plots show the amount that the regions sensitivity to multitasking (peak percent difference between single and multitasks) reduced from pre- to posttraining [(post-multitask − post-single-task) − (pre-multitask − pre-single-task)], for each group separately. Error bars reflect SEM. IPL, inferior parietal lobule; P % SC, peak percent signal change; SMFC, superior medial frontal cortex. **P < 0.035.