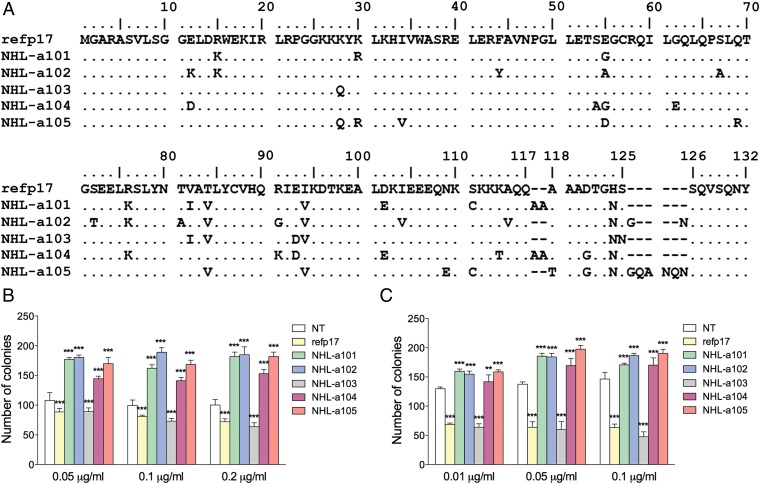
Fig. 1.
Alignment and comparison among amino acid sequences of refp17 and vp17s isolated from HIV–NHL patients and effects of different recombinant p17s on B-cell clonogenicity. (A) Sequences are represented by the single-letter amino acid code. Amino acid positions are referred to the prototype genotype B strain BH10 (UniProtKB P04585; refp17), adopted as reference for this analysis. Each amino acid residue of NHL-derived vp17s not differing from the refp17 sequence is represented by a dot. (B) Raji and (C) BJAB cells were plated in 12-well plates, and after 4 d, medium was replaced by fresh medium with various concentrations, 0.01, 0.05, 0.1, and 0.2 μg/mL of refp17 and lymphoma-associated variants, as indicated. Cells not treated (NT) were used as negative control. The cell growth was analyzed by using 3-[4, 5-Dimethylthiazol-2-y1]-2, 5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (MTT). Data represent the average number of colonies ± SD from three independent experiments performed in triplicate. The statistical significance between control and treated cultures was calculated using one-way ANOVA performed separately for each concentration of p17 variants, across the three groups. Bonferroni’s posttest was used to compare data. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.