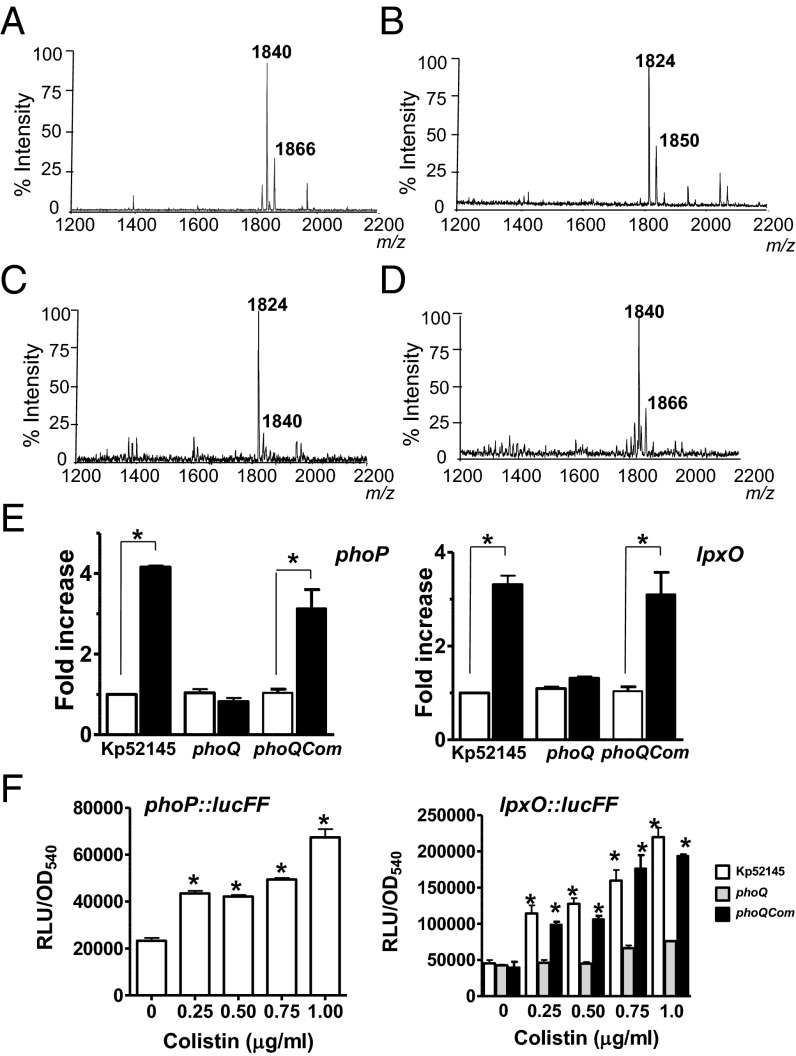
Fig. 6.
Lipid A of colistin-treated bacteria is identical to lipid A expressed by Klebsiella in the lungs. (A) Negative ion MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry spectra from: (A) a representative clinical isolate (no. 2608) of seven strains resistant to colistin grown in LB; (B) its isogenic lpxO mutant; (C) a representative clinical isolate (no. 2615) of seven strains susceptible to colistin grown in LB; and (D) Kp52145 exposed for 1 h to colistin (1 µg/mL) in LB. (E) The transcription levels of phoP and lpxO in colistin-treated Kp52145, 52145-ΔphoQGB (phoQ), or 52145-ΔphoQGBCom (phoQCom) (black bars) were determined by RT-qPCR and are shown relative to the expression levels in mock-treated bacteria (white bars). Results represent means ± SDs. *P < 0.05 (for the indicated comparison, one-way ANOVA); ns, P > 0.05 for the indicated comparison. (F) Luminescence was determined for bacteria carrying the transcriptional fusions phoP::lucFF or lpxO:lucFF exposed for 1 h to different concentrations of colistin. Results are significantly different (**P < 0.01; one-way ANOVA) from the results for nontreated bacteria. In A–D, results are representative of extractions from five independent experiments.