Fig. 4.
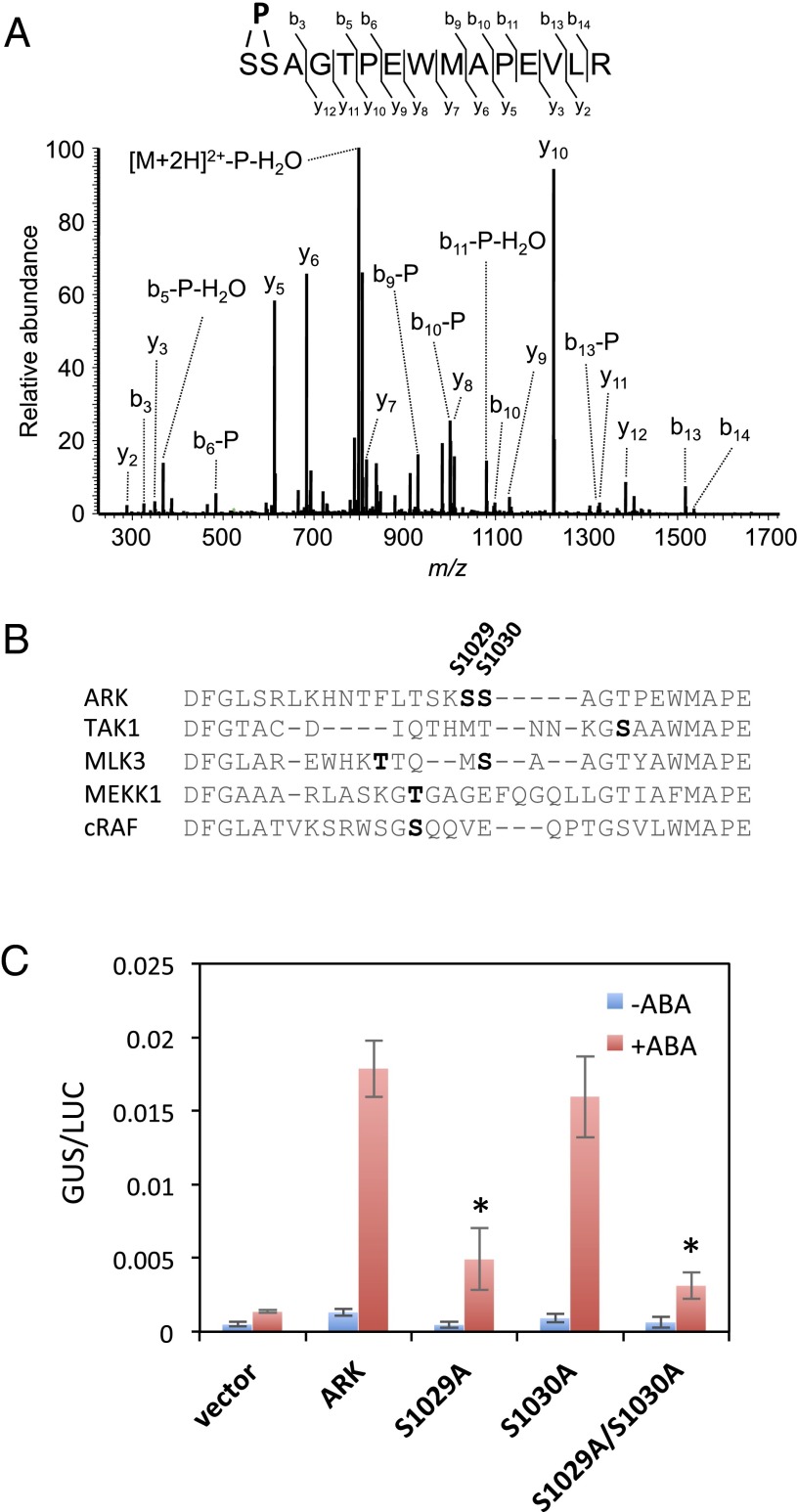
Phosphorylation in the activation loop of ARK is essential for ABA response. (A) MS/MS spectrum of the ARK-derived phosphopeptide found to be increased by ABA treatment in protonemata. Proteins were purified from ABA-treated protonemata of P. patens expressing ARK-GFP by using magnetic beads with the anti-GFP antibody attached. The purified proteins were subjected to digestion with Lys-C and trypsin and analysis by a nanoLC-MS-MS system. Either Ser-1029 or Ser-1030 was predicted to be the site of phosphorylation. (B) Sequence alignment of the amino acids in the activation loop of ARK and mammalian MAPKKKs. Predicted phosphorylation sites for ARK (S1029 and S1030), TAK1 (46), MLK3 (47), MEKK1 (48), and cRAF (49) are indicated by bold letters. (C) Transient assays of AR7 protonemata using constructs of ARK-GFP with or without mutations in the predicted phosphorylation sites. The cDNA was fused to the rice actin promoter and introduced into the AR7 cells with Em-GUS and Ubi-LUC, and the cells were incubated for 1 d with or without 10 µM ABA before protein extraction for the GUS and LUC assays. Levels of gene expression are represented by GUS/LUC ratio. Error bars indicate the SE (n = 3). *P < 0.05 compared with the ARK-GFP–introduced cells (t-test).