Figure 3.
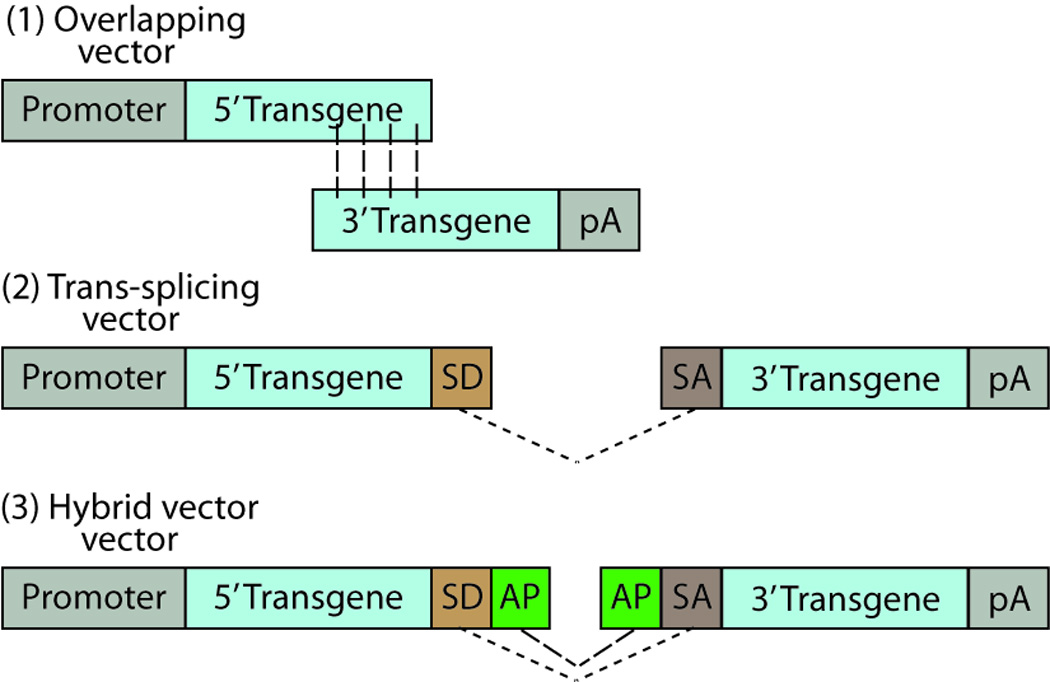
Three AAV dual vector types. (1) Overlapping vectors have a homologous overlapping region between the two halves of the transgene of choice, which undergo homologous recombination for reconstitution of a full-length transcript of the transgene. (2) Trans-splicing vectors undergo splicing through their splice donor (SD) and splice acceptor (SA) sites at the ends of the transgene halves. (3) Hybrid vectors undergo splicing through the SD and SA sites, as well as recombination through a highly recombinogenic site from a exogenous gene, such as alkaline phosphatase (AP). Dashed lines show homologous recombination, dotted lines show splicing between SD and SA sites. Abbreviations: pA, polyadenylation tail; SD, splice donor; SA, splice acceptor; AP, alkaline phosphatase. Adapted from [76].
