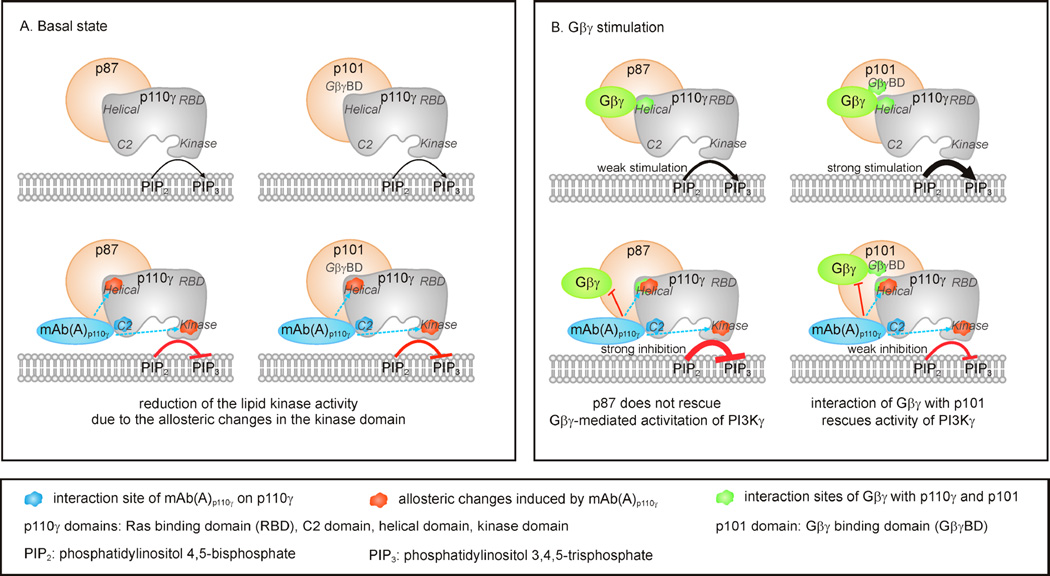
Figure 9. Schematic representation of putative molecular mechanisms induced by mAb(A)p110γ resulting in discriminative inhibition of the PI3Kγ variants.
(A) Effect of mAb(A)p110γ on the basal states of the PI3Kγ variants. Binding of mAb(A)p110γ to the C2 domain mediates allosteric modulation of residues 551–650 in the helical domain and residues 1035–1050 located in the helices kα9 and kα10 of the C-terminal lobe of the kinase domain. These helices play important role in allosteric activation of p110γ, as it was shown in the case of Ras stimulation [35]. mAb(A)p110γ -induced structural change of the kinase domain may interfere and reduce the basal lipid kinase activities of p87-p110γ and p101-p110γ. Slight protection of p101-p110γ basal lipid kinase activity from the inhibitory effect of mAb(A)p110γ is in line with the previous data showing stimulatory modulation of p110γ by p101 independently of its Gβγ adaptor function [41]. (B) Effect of mAb(A)p110γ on the PI3Kγ variants stimulated by Gβ1γ2. Binding of mAb(A)p110γ to the C2 domain of p110γ causes allosteric exposure of a region (residues 551–650) in the helical domain which also includes crucial amino acids involved in interaction with Gβγ, Arg552 and Lys553 [48]. This results in allosteric interference of mAb(A)p110γ with Gβγ binding to p110γ. p101 was shown to be also involved in interaction with Gβγ via putative Gβγ binding domain (GβγBD) located in the C-terminal region of p101 [48]. In contrast to p101, p87 contributed much lesser (if at all) to Gβγ interaction [28,38,41,48]. In the scenario of discriminative inhibition, mAb(A)p110γ disrupts p110γ-Gβγ interaction in a similar way for each PI3Kγ variant, whereas unaltered Gβγ binding capacity of p101 still allows effective translocation of p101-p110γ and regulatory activity. In contrast, p87-p110γ showed reduced capability to interact with Gβγ in the presence of mAb(A)p110γ resulting in drastic reduction of enzymatic activity.
Indicated are phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate (PIP2), phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate (PIP3), the Ras binding domain (RBD, residues 220–311), the C2 domain (residues 357–522), the helical domain (residues 545–725), the kinase domain (residues 726–1092) of p110γ [58], and putative Gβγ binding domain (GβγBD) of p101 [48].