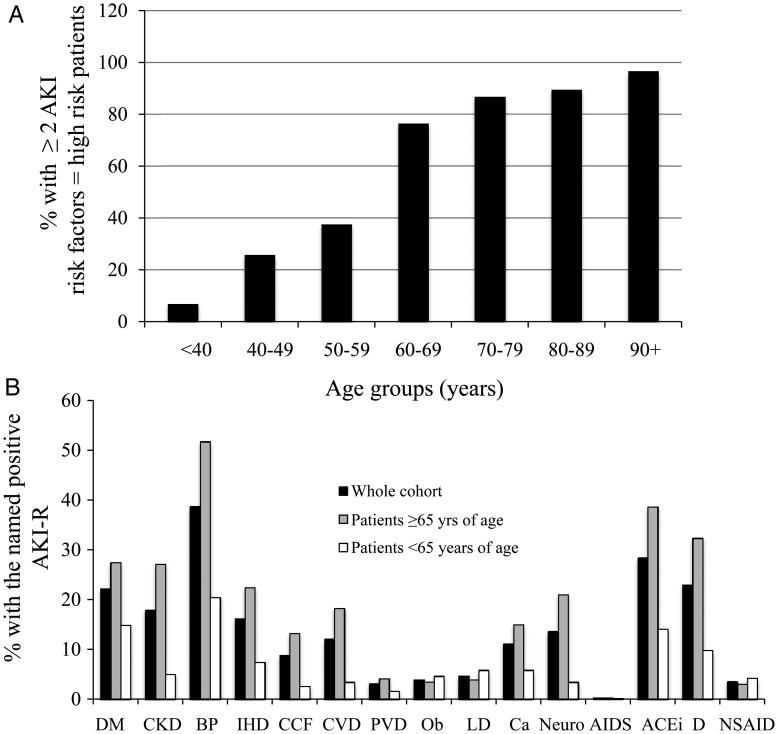
Fig. 2.
(A) Age-dependent distribution of patients at high risk of AKI. High risk of AKI was defined as the presence of two or more fixed patient-related AKI risk factors. (B) Individual AKI risk factor (AKI-R) distribution. (B) Percentage of patients (solid black bars), patients ≥65 years of age (grey bars) or patients <65 years of age (open bars), positive for each of the individual fixed patient-related AKI risk factors. DM, diabetes mellitus; CKD, chronic kidney disease; BP, hypertension; IHD, ischaemic heart disease; CCF, congestive cardiac failure; CVD, cerebrovascular disease; PVD, peripheral vascular disease; Ob, morbid obesity; LD, liver disease; Neuro, neurological or cognitive impairment; AIDS, known diagnosis of AIDS; ACEi, angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor; D, prescription of diuretic; NSAID, prescription of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs).