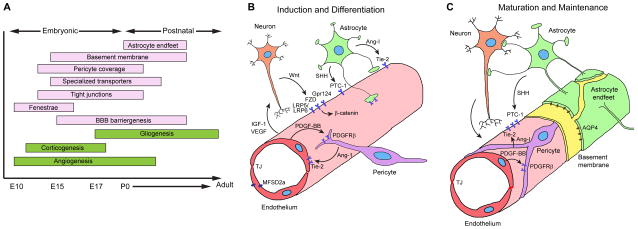
Figure 2. Blood-brain barrier development in the murine central nervous system.
A. Developmental timeline. Restriction of paracellular and transcellular transport of solutes is accomplished by elimination of endothelial fenestrae and pinocytosis, formation of a continuous endothelial monolayer connected with the tight junctions, creation of highly selective endothelial transport systems, and establishment of specialized perivascular structures, including the basement membrane and the coverage of the endothelial capillary wall by pericytes and astrocytic endfeet. E, embryonic days; P, postnatal days.
B. Induction and differentiation. Wnt ligands (Wnt7a/7b) secreted by neural cells bind to endothelial Frizzled receptors (FZD) and co-receptors low-density lipoprotein receptor-related protein (LRP) 5 and 6, which activate β-catenin signaling, leading to the induction of BBB specific genes. G-protein coupled receptor 124 (Gpr124) co-activates Wnt/β-catenin signaling. Endothelial cells secrete platelet-derived growth factor BB (PDGF-BB), which interacts with platelet derived growth factor receptor-β (PDGFR-β) in pericytes, inducing pericyte recruitment. Pericytes and astrocytes secrete angiopoietin-1 (Ang-1) that acts on endothelial Tie-2 receptor leading to microvascular maturation and highly stable and impermeable BBB. Pericytes are required for the expression of endothelial major facilitator superfamily domain-containing protein 2a (MFSD2a) that is critical for the BBB formation and maintenance. Astrocytes secrete sonic hedgehog (SHH) that acts on endothelial patched homolog 1 (PTC-1) receptor eliciting signaling which contributes to the BBB formation. Endothelial cells secrete vascular growth factor (VEGF) and insulin growth factor (IGF-1) contributing to proper neurovascular patterning. Additional signal transduction pathways may also participate in BBB formation. TJ, tight junction.
C. Maturation and maintenance. Postnatally, brain capillaries are covered by mature pericytes sharing the basement membrane with endothelium. Astrocytic endfeet form the outer layer of the mature capillaries. Peri-cytes and astrocytes continue secreting matrix proteins (yellow) of the basement membrane. Signaling pathways mediating BBB induction and differentiation likely continue to play a role in BBB maturation and maintenance and their dysregulation may lead to BBB breakdown causing different central nervous system pathologies. AQP4, aquaporin-4 water channel.