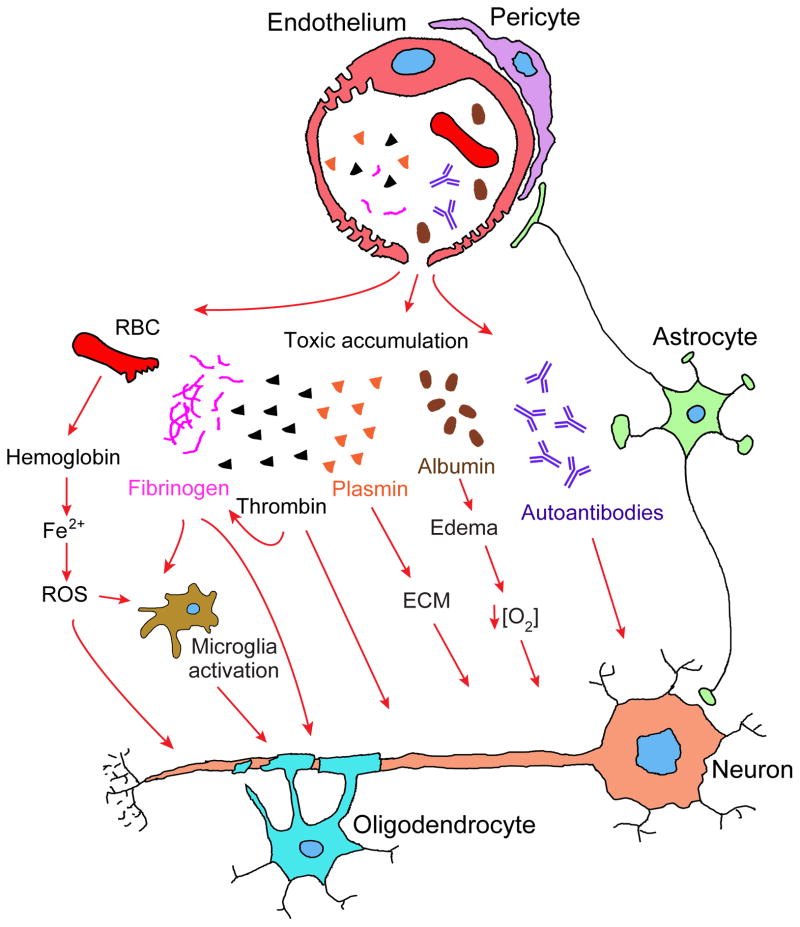
Figure 4. Vascular-mediated neurodegeneration.
Aberrant pericyte-endothelial or astrocyte-pericyte signal transduction leads to BBB breakdown resulting in brain accumulation of 1) red blood cell (RBC)-derived neurotoxic hemoglobin and iron (Fe2+) causing production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) and oxidant stress to neurons; 2) neuronal toxic blood-derived proteins such as fibrinogen, thrombin, and plasminogen, which could be converted into plasmin that in turn degrades neuronal extracellular matrix (ECM) and leads to detachment of neurons and cell death; 3) fibrinogen that activates microglia, promotes neuroinflammation and demyelination, and prevents myelination by oligodendrocyte progenitor cells; 4) albumin that contributes to the development of vasogenic edema, capillary hypoperfusion and hypoxia. BBB breakdown can also lead to the loss of immune privilege resulting in development of anti-brain antibodies against different axonal and membrane components of neurons.