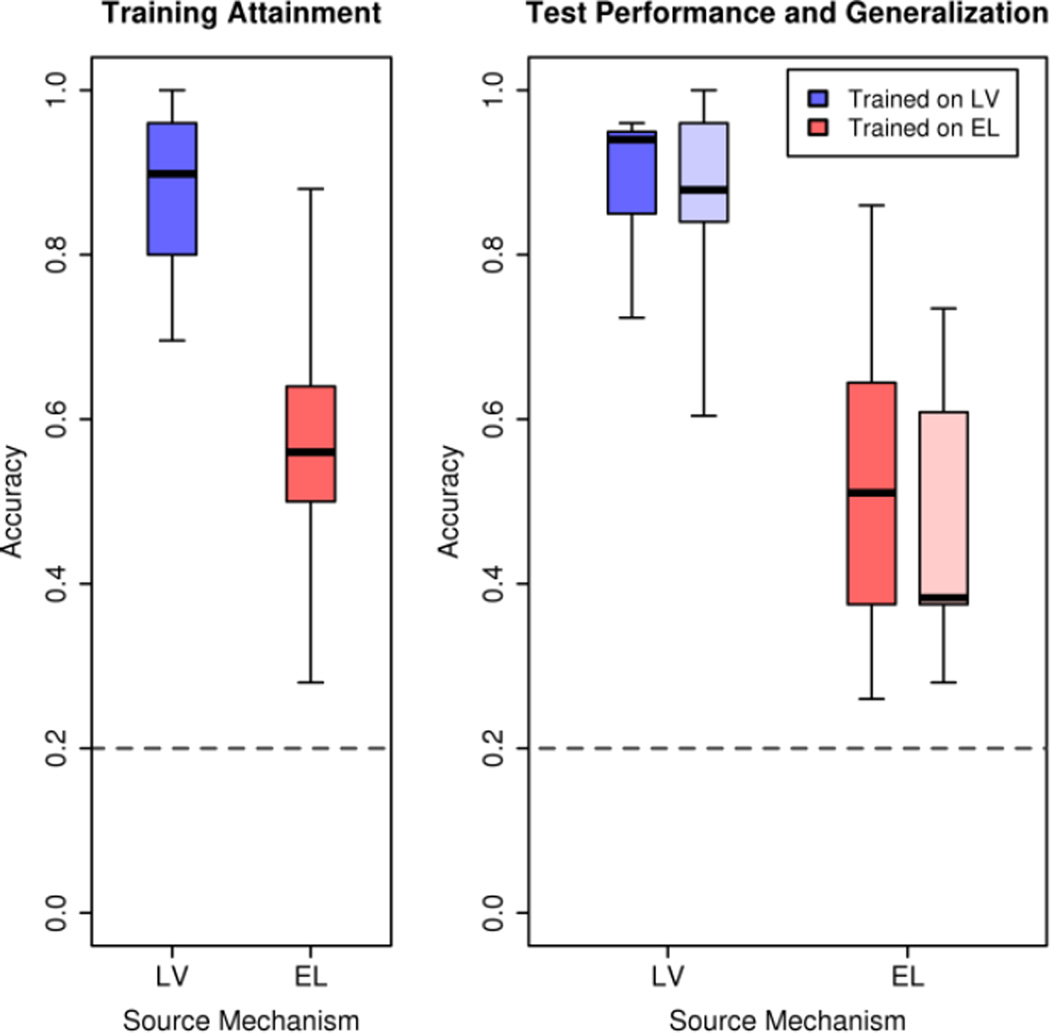
Fig 2. Learning talker identity from laryngeal and electrolarynx sources.
Listeners learned talker identity successfully from both laryngeal (LV) and electrolarynx (EL) vocal sources, but were significantly more accurate at learning talker identity from a laryngeal source. For both vocal sources, listeners are significantly more accurate at identifying talkers from familiar sentences (darker boxes) than from novel ones (lighter boxes). Horizontal dashed line indicates chance (20%). Boxplots: Solid horizontal bar represents the median; colored area: interquartile range; dashed whiskers: maximum and minimum values.