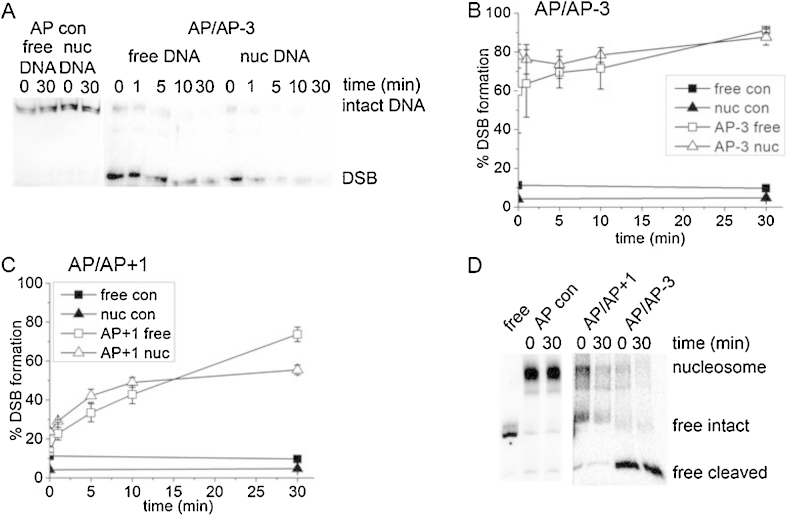
Fig. 3.
Cleavage of two bistranded AP sites by 1 μg CHO-K1 nuclear extract. (A) Representative phosphorimaging scans of native polyacrylamide gels showing the formation of DSB in bistranded cluster (AP/AP − 3) in both free and nucleosomal-bound DNA substrates following treatment with 1 μg CHO-K1 nuclear extract for given times. Strand 2 within the DNA duplex was 5′-end labelled with 32P. The DSB band represents DNA that has been cleaved at both AP sites. A single AP site in strand 2 (AP con Table 1) does not give DSB when incubated with extract. (B) Percentage formation of DSB from AP/AP − 3 substrate: (open square) AP/AP − 3 free DNA, (open triangle) AP/AP − 3 nucleosomal-bound DNA and no extract control for both AP/AP − 3 free DNA (filled triangle) and nucleosomal-bound DNA, (filled square). (C) Percentage formation of DSB from AP/AP + 1 substrate: (open square) AP/AP + 1 free DNA, (open triangle) AP/AP + 1 nucleosomal-bound DNA and no extract control for both AP/AP + 1 free DNA (filled triangle) and nucleosomal-bound DNA, (filled square). (D) Representative phosphorimaging scan of a native polyacrylamide gel showing the nucleosome stability after DSB formation resulting from treatment with 1 μg CHO-K1 nuclear extract for 0 and 30 min. The positions of the nucleosome, free DNA remaining intact and free DNA, that has been cleaved by the nuclear extract, are indicated. A single AP site in strand 2 (AP con Table 1) is stable when incubated with extract. The nucleosomes were loaded onto the gel without deproteinization. A sample of free DNA was included for comparison. Error bars represent standard deviation determined from at least three independent experiments.