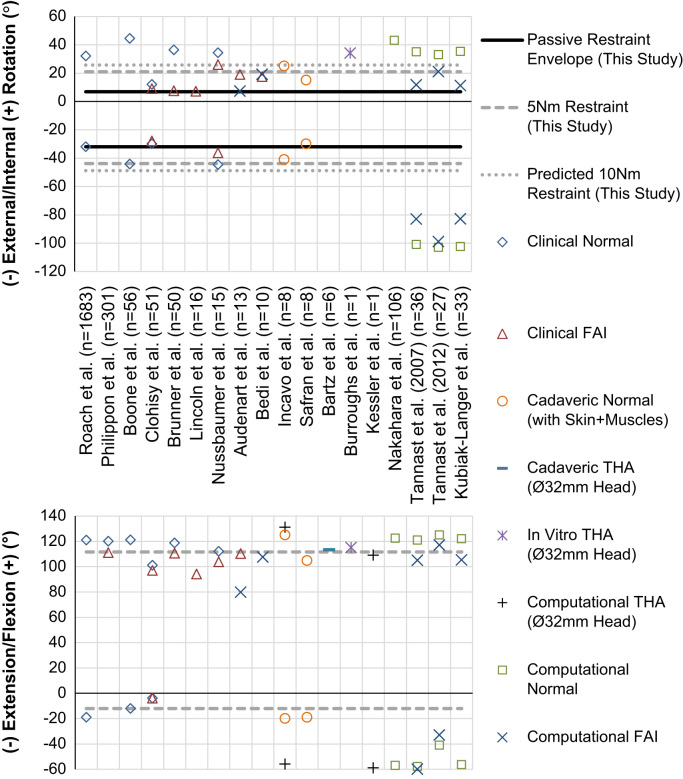
Fig. 7.
A comparison between clinical, experimental and computational range of motion measurements and the results from the present study for internal and external rotation at 90° flexion with neutral ab/adduction (top), and for flexion/extension (bottom). It can be seen that the passive restraint envelope (for un-resisted rotation) measured in the present study was within clinical measurements for normal subjects, compares well to previous cadaveric work, and was always less than results from studies which only considered bony impingement as a limit to hip rotation (computational studies). The predicted 10 N m restraint values were calculated using the mean torsional stiffness measured at 5 N m restraint.