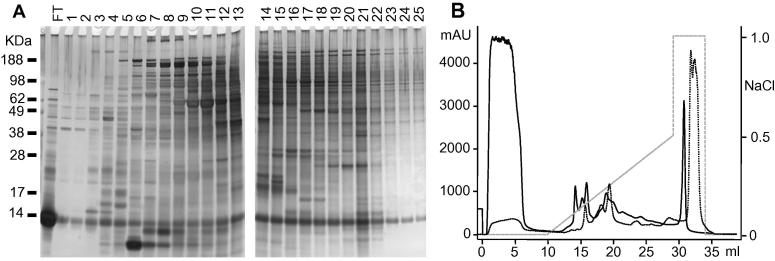
Fig. 2.
The separation of Dermanyssus gallinae soluble mite extract using ion exchange chromatography. Soluble mite extract was separated using a 1 ml HiTRAP Q HP anion exchange column (GE Healthcare) and eluted with an increasing NaCl gradient. (A) PAGE separation of unbound column flow-through material and sequentially eluted fractions (1–25) obtained from the ion exchange chromatography of soluble mite extract from fed mites. Proteins were electrophoresed on a 12% Bis–Tris Novex gel (GE Healthcare) and silver stained (SilverQuest, Thermo Fisher Scientific). (B) Chromatograms of the ion exchange chromatography elution profiles of soluble mite extract derived from fed mites (solid line) and starved mites (dotted line) soluble mite extract. The figure depicts the absorbance (mAU at 280 nm) of elution of the unbound flow-through (FT, 0–10 ml) and the 25 sequentially eluted 1 ml fractions (10–35 ml). The broken grey line represents the NaCl content of the elution buffer (moles per litre), which is given on the secondary Y axis (NaCl).