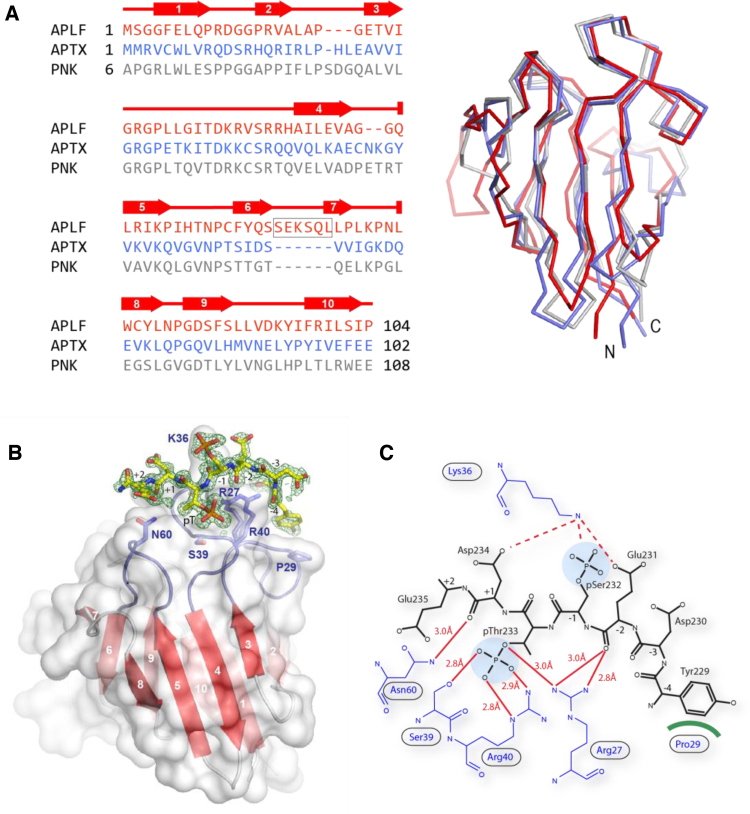
Fig. 3.
Structure of APLF-FHA:XRCC4 phosphopeptide complex.
(A) Sequence alignment and superposition of Cα backbone structures of the APLF FHA domain (red) aprataxin FHA domain (blue) PNKP FHA domain (grey). The positions of β-strands are indicated by arrows above the sequence alignment and the five residue insertion between β6-7 is boxed. (B) Ribbon representation showing the 10 β-strands as red arrows with the molecular surface superimposed. Loops β3–β4 and β5–β6 involved in peptide binding are blue. Seven residues of an XRCC4-derived peptide are shown in stick representation modeled into 2Fo-Fc density. The phosphothreonine binds in the canonical binding pocket whilst phosphoserine protrudes directly away from the FHA domain surface. (C) Schematic representation of protein-peptide contacts between APLF FHA and triphosphorylated XRCC4 peptide. Hydrogen bonds and van der Waals interactions are denoted by red lines and green crescents respectively.