Fig. 5.
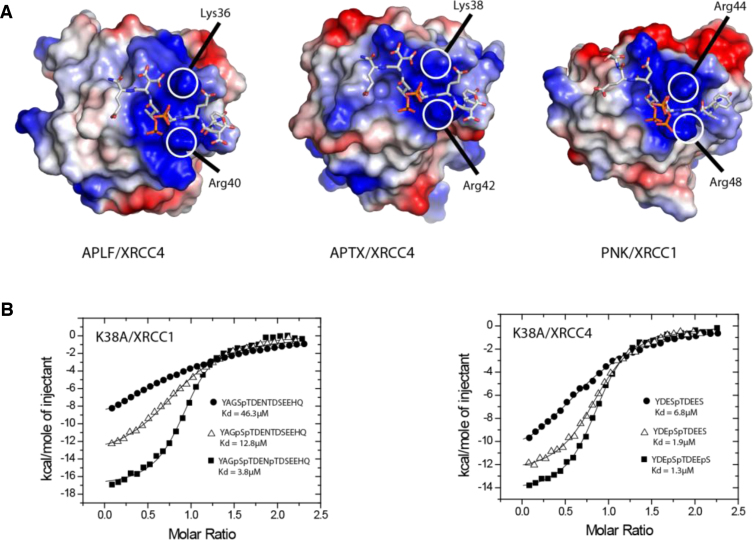
Contribution of basic residues to phosphopeptide binding.
(A) Comparison of the electrostatic potential surfaces at the phosphopeptide-binding sites of the APLF, aprataxin (APTX) and PNKP FHA domains. The structure of the aprataxin/XRCC4 complex was modelled on the basis of an overlap of the X-ray structure of the isolated FHA [40] with that of the APLF complex (this study). (B) Effect of aprataxin Lys38 mutation on XRCC1 and XRCC4 phosphopeptide binding. Binding is decreased relative to the wild-type 2.7-, 8.5 and 8.8- fold respectively for mono-, di- and tri-phosphorylated XRCC1 peptides and 3.2-, 7.6- and 9.3-fold respectively for XRCC4 peptides.