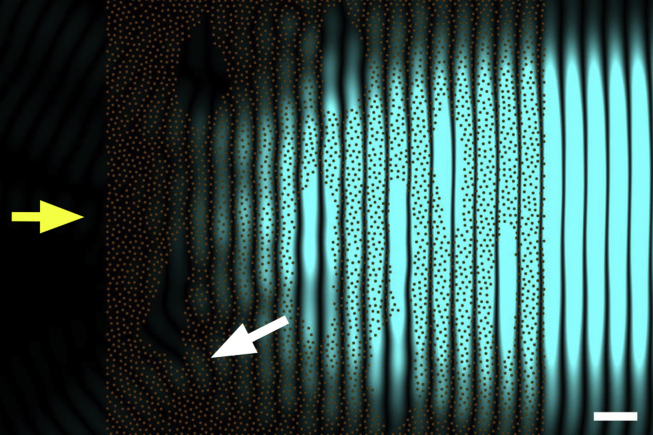
Fig. 8.
The effect of fibril voids on light transmission. Secondary waves from the same collagen fibril distribution shown in Fig. 6. As before, primary incoming light is travelling from left to right (yellow arrow), with a wavelength of 500 nm. Collagen fibrils in transverse sections are represented by brown circles. Regions devoid of fibrils are now present (lakes). The intensity of the secondary radiation arising from the fibrils is shown in blue. Even in this case, backwards secondary radiation is evident in the figure (white arrow). Bar 500 nm.