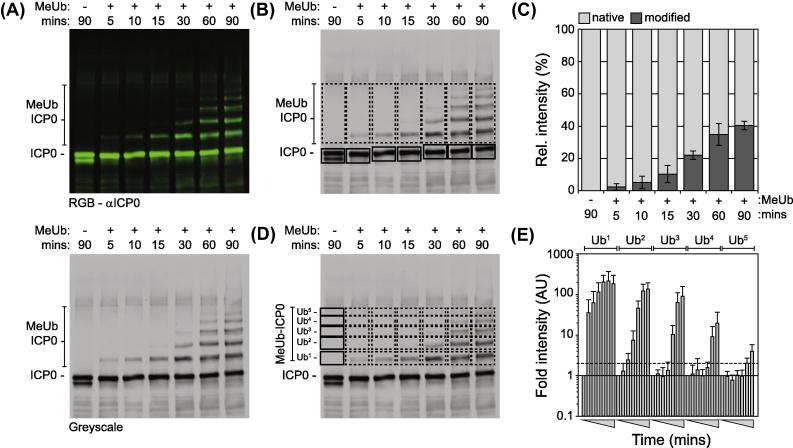
Fig. 3.
Quantitation of ICP0 auto-ubiquitination activity using near-IR imaging. Equivalent reaction mixtures (as described in Fig. 2) were activated by the addition of methylated-ubiquitin (±MeUb: a ubiquitin derivative unable to support poly-ubiquitin chain formation) and incubated for the specific times (mins) at 37 °C. Reaction mixtures were analyzed by western blotting for ICP0 auto-ubiquitination (MeUb ICP0; mAb 11060 and Dylight anti-mouse 800). (A) Representative image of a scanned immunoblot showing RGB and corresponding single channel grayscale image (top and bottom panels, respectively). (B) ROI relating to unmodified ICP0 (native; solid boxes) and total auto-ubiquitinated ICP0 (modified; dashed boxes) were quantified for their respective signal intensities and normalized with respect to equivalent areas of the membrane in the negative control (90-min time point in the absence of ubiquitin) within individual experiments. Bar graph depicts the relative intensity of native (light gray bars) to modified (dark gray bars) ICP0 as a proportion of the total signal intensity (%). Means and standard deviations in modified ICP0 signal intensity from three independent experiments are shown. (C) ROI relating to single lysine mono-ubiquitination events within ICP0 (dashed boxes; Ub1–Ub5) were individually quantified and normalized with respect to equivalent areas of the membrane in the negative control (90 min in the absence MeUb; solid boxes). Bar graph depicts the relative fold increase in individual lysine mono-ubiquitination within ICP0 over the time course of analysis (gray triangles). Black line depicts baseline following background normalization. Gray dotted line represents one standard deviation from background. Means and standard deviations from three independent experiments are shown. Images shown are representative and taken from a single experiment.