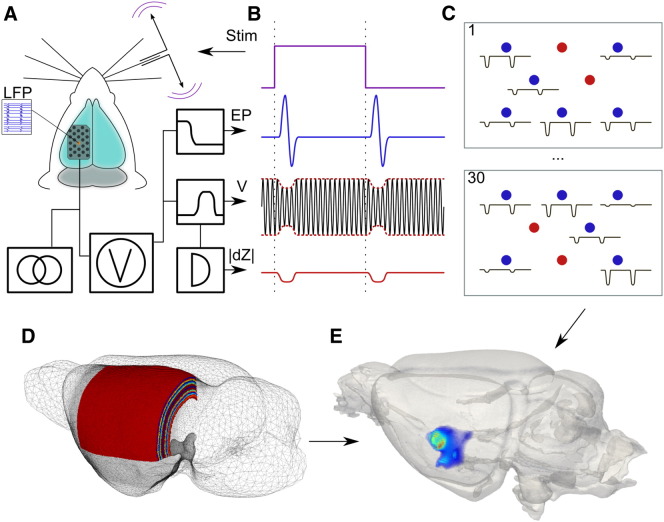
Fig. 1.
Method and paradigm. A) The 30 electrode array was placed over the exposed left S1 cerebral cortex. A 16 contact local field potential (LFP; orange dot) probe was placed through the center of the array over the activated whisker barrel group determined by intrinsic optical imaging. B) Impedance acquisition. The whiskers contralateral to the electrode array were moved forward and backward every second (stimulation waveform — Stim) and 15 cycles averaged for each impedance measurement. A constant amplitude current of 50 μA at 1725 Hz was injected through selected pairs of electrodes. The resulting voltages were recorded on all other 28 electrodes with respect to a reference in the contralateral scalp, low pass filtered at 400 Hz to yield evoked potentials (EP), and band pass filtered at 1725 ± 500 Hz to yield an amplitude modulated sine wave (V), which was demodulated to reveal the impedance change (|dZ|). C) This sequence was repeated for all 30 electrode injection pairs. The 1st and 30th injection pairs are illustrated. Red — injection pair; blue — resulting impedance decreases. Images were reconstructed using a 5 M element FEM tetrahedral mesh segmented into layers orthogonal to somatosensory cortex (D), and the resulting data stored in 4D spatiotemporal format (E).