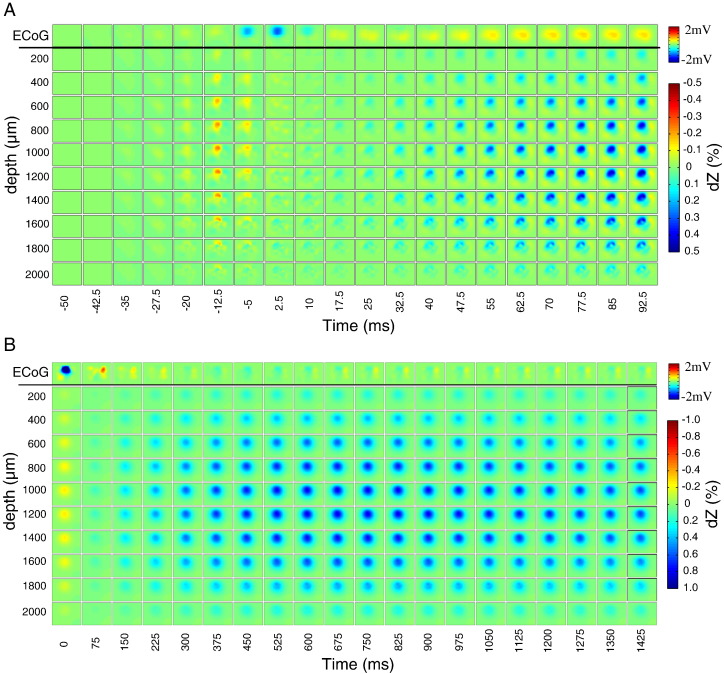
Fig. 5.
Volumetric reconstruction of impedance changes from data shown in Fig. 4. Each tile is a raster image showing the estimated impedance change at a specific depth (rows; range 0.2–2 mm) and time point (columns). The first row shows the simultaneous ECoG map smoothed with a Gaussian filter (standard deviation = half the distance between adjacent electrodes). Tiles are rotated by 90° clockwise relative to the electrode maps shown in Fig. 3. (A) Impedance changes and ECoG map between − 50 ms and 92.5 ms around IIS peak. Fast impedance decreases can be seen around − 12.5 ms, and slow impedance increases start around 32.5–40 ms. (B) Impedance changes and ECoG map between 0 and 950 ms.