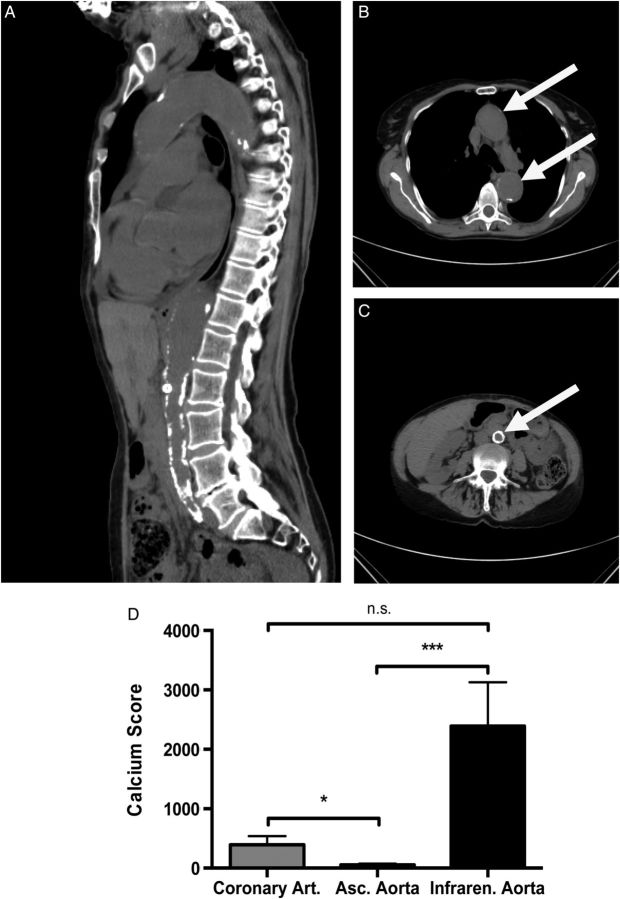
FIGURE 7:
Uraemic media calcification in patients with chronic kidney disease. Representative CT images with a sagittal reconstruction (A) and a transverse section of the thoracic (B) and abdominal aorta (C) are shown in a patient with chronic kidney disease Stage IV (estimated glomerular filtration rate of 28 mL/min/m2) due to hypertensive nephropathy. The white arrow indicates the position of the aorta. (D) In a cohort of 36 in patients with end-stage renal failure, the calcium scores of the ascending aorta (white bar), the coronary (grey bar) and infrarenal aorta with the common iliac arteries (black bar) were measured by native CT scans. The calcium score of the ascending thoracic aorta was significantly lower, when compared with the calcium scores of the abdominal aorta or coronary arteries, respectively. Data are given as means ± SEM. n.s., not significant. * indicates a P-value <0.05, *** indicates a P-value <0.001.