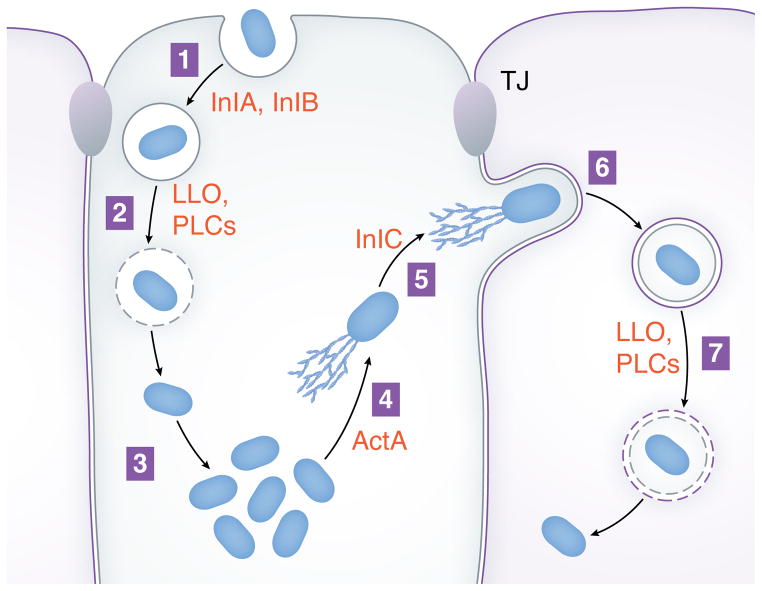
Figure 1. Intracellular life cycle of Listeria.
Steps in the infection cycle are (1) internalization of bacteria into host cells, (2) escape from phagosomes, (3) replication in the cytosol, (4) actin-based motility, (5) formation of protrusions, (6) engulfment of protrusions, and (7) dissolution of the double membranous vacuole. The process of cell-to-cell spread comprises steps 4–7. Bacterial factors that promote various steps in the life cycle are in red lettering. ‘LLO’ denotes Listeriolysin O, and ‘PLCs’ indicates the phospholipases PlcA and PlcB. ‘TJ’ represents tight junctions.