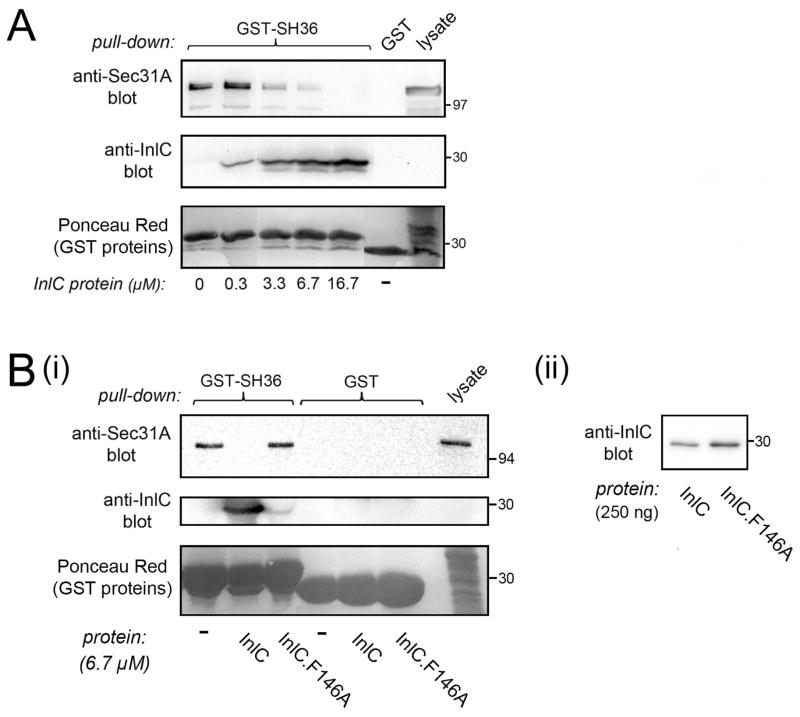
Figure 6. InlC displaces Sec31A from the Tuba SH36 domain.
A. InlC-mediated inhibition in association of Sec31A with the SH36 domain. A constant amount of lysate from Caco-2 BBE1 cells was incubated with approximately 0.30 μM GST-SH36 and increasing concentrations (0–16.7 μM) of purified InlC. Sec31A in GST-SH36 precipitates was detected by Western blotting. The image is of a spliced gel in which irrelevant lanes had been excised. B. Control with the mutant protein InlC.F146A. (i). Caco-2 BBE1 cell lysates were incubated with approximately 0.30 μM GST-SH36 in the absence of competitor (−) or in the presence of 6.7 μM of InlC or InlC.F146A protein. GST alone (0.30 μM) was used as a negative control. Sec31A in precipitates was detected by Western blotting. Binding of InlC to GST-SH36 was confirmed by probing a stripped membrane with anti-InlC antibodies. (ii). Anti-InlC Western blot of purified wild-type and mutant InlC proteins. This experiment verified that the InlC.F146A protein does not have diminished reactivity to anti-InlC antibodies. Data in A and B are each representative of three experiments.