Fig. 4.
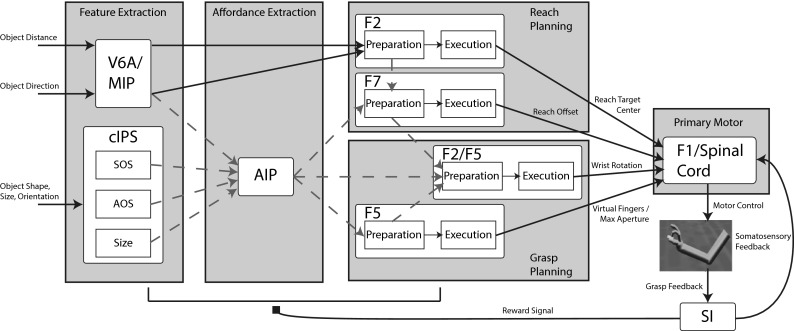
An overview of the ILGA model. Connections modifiable by reinforcement learning are shown in dashed lines. The parietal regions MIP and V6A provide the premotor region F2 with object position information to plan the reach. V6A, MIP, and the cIPS populations project to AIP, which projects to the signal-related populations of the other premotor regions. Each premotor region selects a value for the parameter it encodes and projects to the primary motor region F1 which controls the movement. The reach planning is performed by area F2 which represents the center of the target object and F7 which selects the reach offset. Grasp planning is performed by area F5 which selects the virtual fingers and maximum grasp aperture and F2/F5 which selects the wrist rotation. Grasp feedback is returned to somatosensory area S1 which provides the reinforcement signal to the model and somatosensory feedback to F1. Preparation-related premotor populations plan the reach and excite corresponding execution-related premotor populations. Each execution-related premotor population additionally receives tonic inhibitory inhibit (not shown) that is released when a go signal is detected, triggering the performance of the reach and grasp
