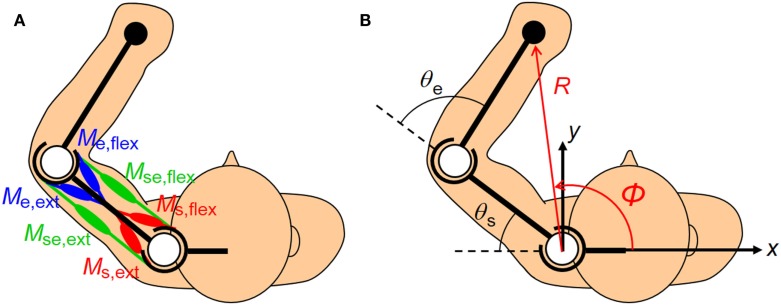
Figure 2.
Human upper limb model. The human musculoskeletal structure of an upper limb is simplified as a two-link model with six muscles. (A) Three pairs of agonist–antagonist muscles are arranged around the shoulder and elbow joints. The paired muscles are indicated in the same color (red, green, and blue). The mono-articular muscle pair around the shoulder joint (Ms,ext and Ms,flex), bi-articular muscle pair around the shoulder and elbow joints (Mse,ext and Mse,flex), and mono-articular muscle pair around the elbow joint (Me,ext and Me,flex) are responsible for coordinating and regulating the shoulder and elbow joint movements to control hand movement. (B) The hand position in the planar task space can be defined in Cartesian coordinates (x, y) or polar coordinates (R, φ) centered on the shoulder. Note that the polar coordinates (R, φ) are defined as positive when the endpoint moves away from the base of the body. These coordinates are the functions of the shoulder and elbow joint angles (θs, θe).