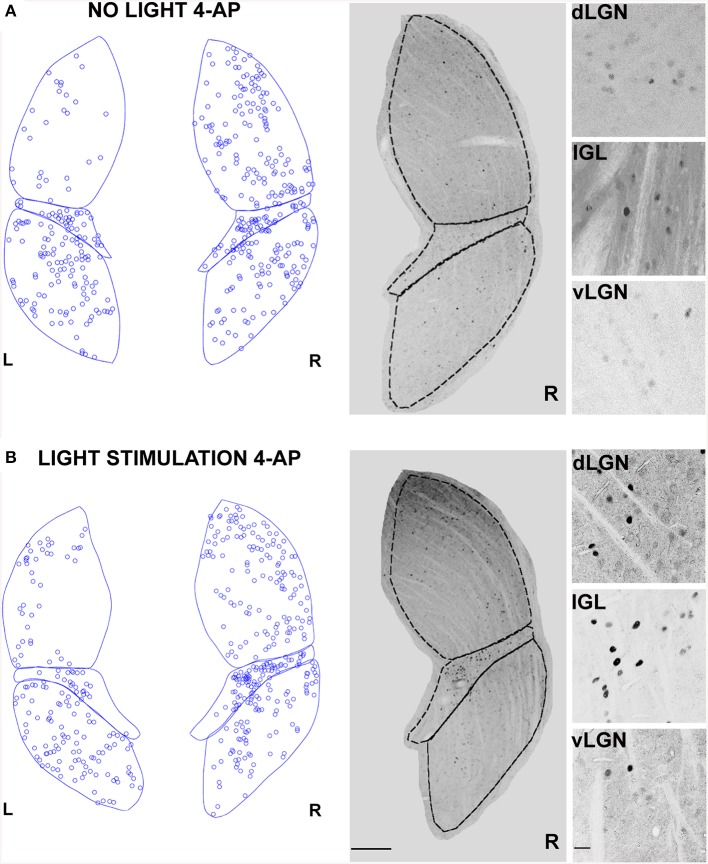
Figure 5.
Changes in LGN activity by intravitreal injection of 4-aminopyridine (4-AP). (A,B) Representative immunostainings (right) and digital reconstructions (left) of the right (R) and left (L) LGNs (same coronal sections). Circles report the location of identified c-Fos positive cells (for segmentation algorithm, see Materials and Methods). In these experiments the A-type potassium channel blocker 4-aminopyridine was injected in the left eye vitreal chamber (2 mM). (A) An exemplar result to illustrate the effect of 4-AP on c-Fos activation pattern in the no-light condition (animal kept in darkness). (B) The effect of ON-OFF light activation in the presence of 4-AP. Light-stimulation was obtained with alternating black and white vertical bars at constant overall luminance (white bars 37 mW/m2; black bars 0.11 mW/m2; 2 h; 2 Hz refresh rate; 0.5 cycle/degree; left eye stimulation). The three small panels on the right are magnification of the dLGN, IGL, and vLGN from the corresponding sections. Continuous and dashed lines indicate edges of dLGN, IGL, and vLGN. Notice how while 4-AP increases the basal activation of the dLGN (see data in the text, also compare L and R), the effect of light stimulation on this structure is not noticeable (Compare R in A with B). Calibration bar is 200 μm for the large immunostaining panels and 50 μm for the small insets.