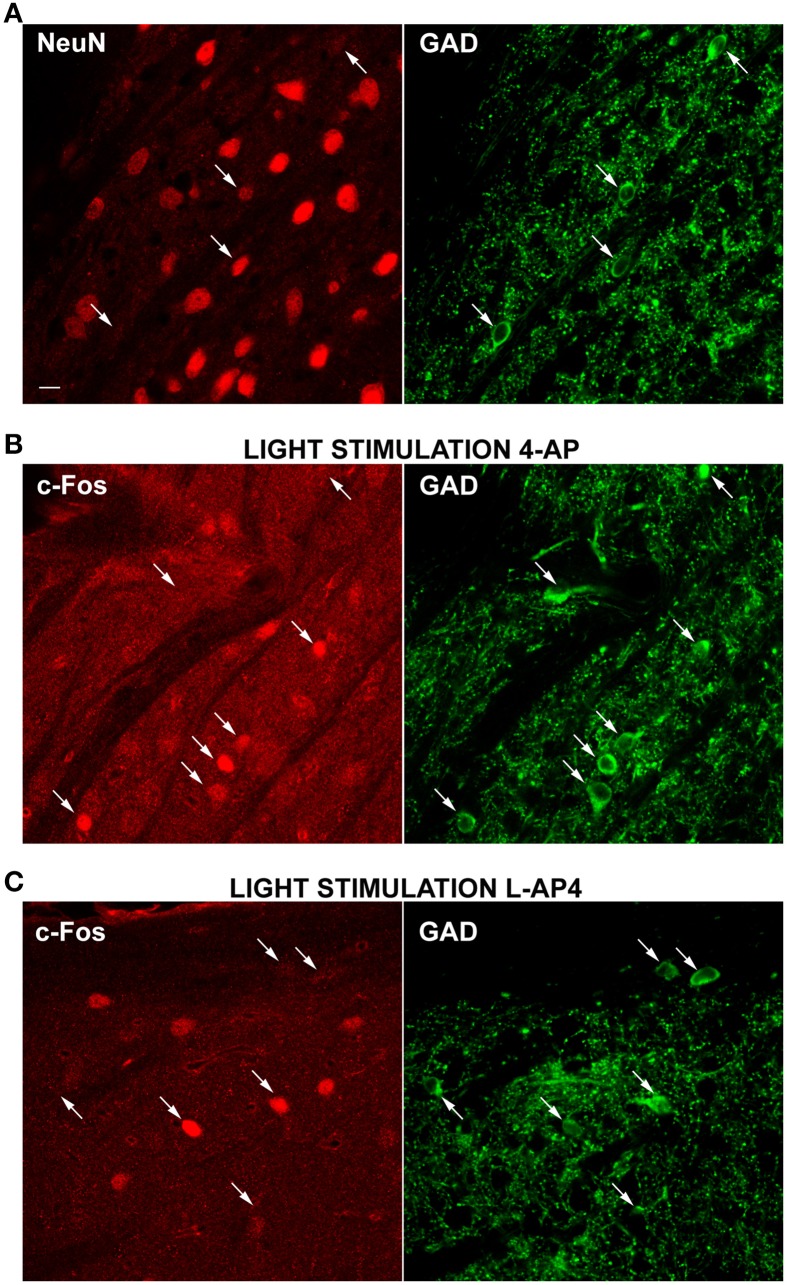
Figure 8.
Differential activation of GAD positive neurons by 4-AP and L-AP4. (A–C) Double-immunolabelings of the dLGN for the neuronal cell marker NeuN (left) and GAD (right), the synthesizing enzyme of GABA (A) and for the activity marker c-Fos (left) together with GAD (right) (B,C). A mix of GAD65 and 67 antibodies was used to better visualize GABAergic neurons. Notice how a strong GAD fluorescence is present in the somatic cytosol, whereas nuclei are unstained. Puncta are the dendritic and axonal arborisations of these interneuronal cells. In Panel A, arrows point to some exemplars GABAergic neurons which are in most cases either NeuN negative or weakly positive (3 out of 4 cells). Images presented (B,C) were obtained from the dLGN of animals injected into the eye with 4-AP (2 mM; B) and L-AP4 (2 mM; C) and stimulated contralaterally with ON-OFF light patterns. Notice the differential activation of GAD positive cells in the two experimental conditions. With 4-AP (B), of the seven GAD positive cells indicated by arrows, five are strongly c-Fos positive (C), of the six GAD cells indicated by arrows, only two are active. Magnification, 63×. White calibration bar, 10 μm.