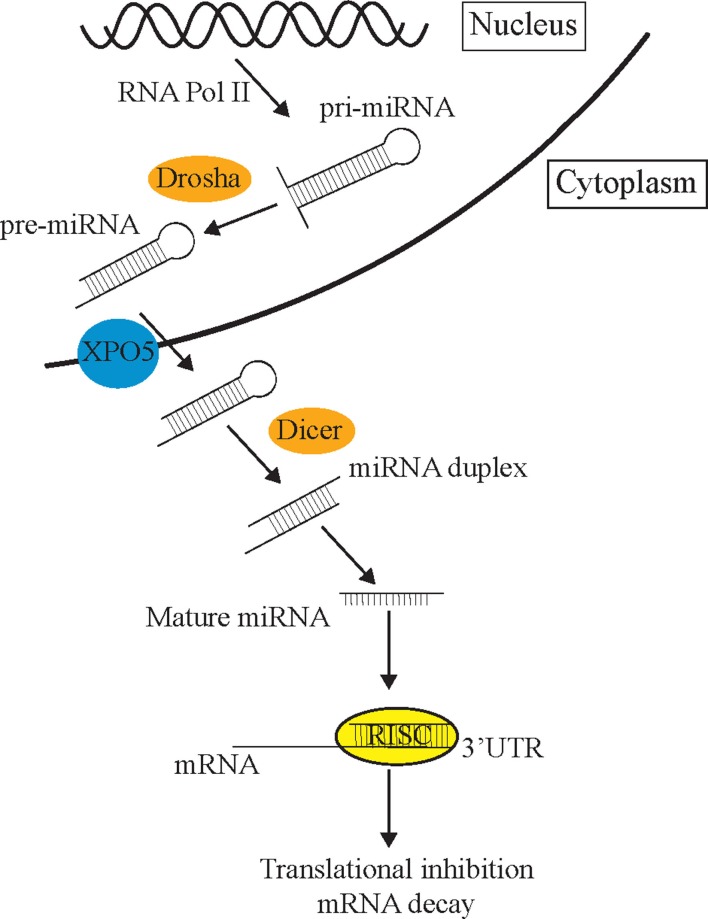
Figure 1.
The miRNA pathway. Primary miRNAs (pri-miRNAs) are transcribed from the genome and form hairpin structures. Nuclear-localized Drosha endonuclease cleaves pri-miRNAs into approximately 70 nt precursor miRNAs (pre-miRNAs) which are then transported from the nucleus to the cytoplasm by Exportin-5 (XPO5) via the nuclear pore complex, where they are further cleaved by Dicer into mature 21–23 nt miRNA fragments. Once the strands separate, the guide strand is loaded into the RISC complex (AGO and different cofactors) to scan the transcriptome for partial complementary target transcripts. These sequences are either repressed by the RISC complex or degraded in P-bodies.