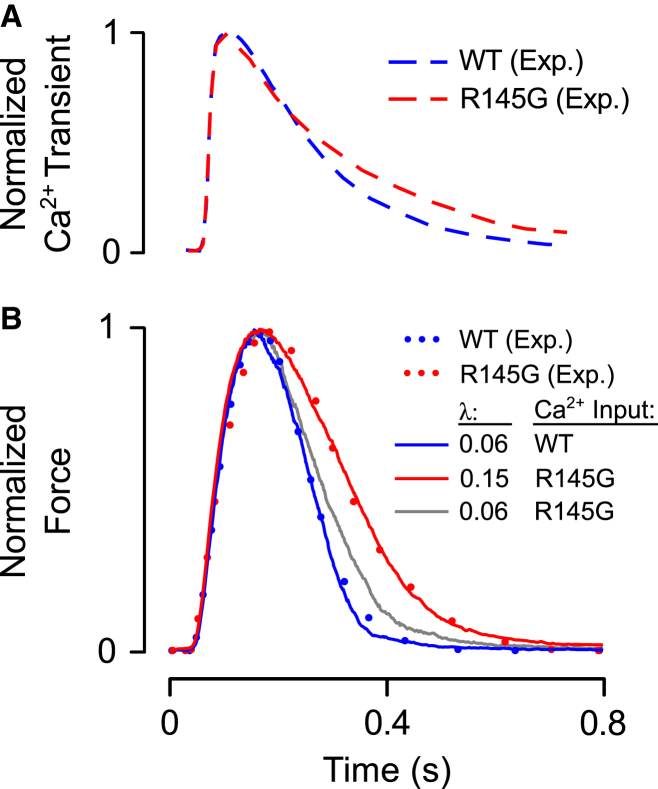
Figure 8.
Analysis of the functional consequences of the TnI mutation R145G. (A) Ca2+ transients were digitized from a study of papillary muscles taken from WT mice and R145G mutants by Wen et al. (22). (B) Simulated twitch responses (solid traces) were obtained by driving the model with Ca2+ transients shown in (A). Model parameters were adjusted until output force (blue trace) matched a measured WT twitch record (blue dots). The fitted parameters are reported in Table 1, set 3. Then, driving the model with the R145G transient, the parameter λ was increased to determine whether this change was capable of explaining the effects of the mutation. Increasing λ from 0.06 to 0.15 allowed the model (red trace) to reproduce the measured R145G twitch record (red dots). To illustrate that the change in λ exerted substantial effects on twitch independent of the differences in WT and R145G Ca2+ transients, λ was set to 0.06 once again and the model was driven with the R145G transient (gray trace). To see this figure in color, go online.